Viewing a process
Prerequisite
- Access to the View > Process (PM023) menu.
Introduction
The process view menu allows performing quick and efficient searches on the data of created processes.
Below, see further details on how to perform view operations:
Viewing a process
1. To view the data of a process, access the Process (PM023) menu.
2. Use the search filters to look for the desired process and click on the Search button.
3. Select the process in the list of records and expand the  button.
button.
4. Choose whether you wish to view the process flowchart or the process data screen.
In addition to viewing the flowchart and the process data screen, it is possible to check other information.
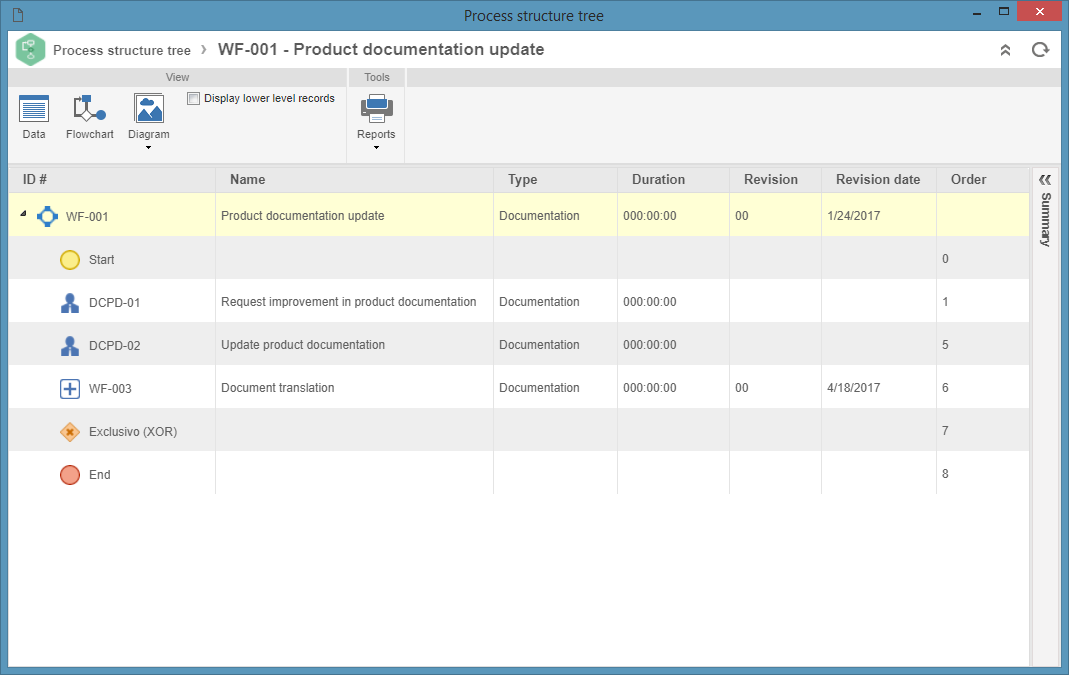
Process tree
The process tree is viewed through the  button (view process tree), located on the toolbar of several system screens (mentioned in this documentation).
button (view process tree), located on the toolbar of several system screens (mentioned in this documentation).
On this screen, it is possible to view the data of a certain process as a tree.
See a process tree example below:
Input and output diagram
See how to generate the diagram of process inputs, outputs, and stakeholders:
1. On the screen that has the respective feature (Activity/decision creation, Process creation, Process view, Activity/decision view, To-do task view, and Flowchart), locate and select the desired process.
2. Then, click on the  toolbar button. At this point, the input and output diagram screen will be displayed. See the example:
toolbar button. At this point, the input and output diagram screen will be displayed. See the example:
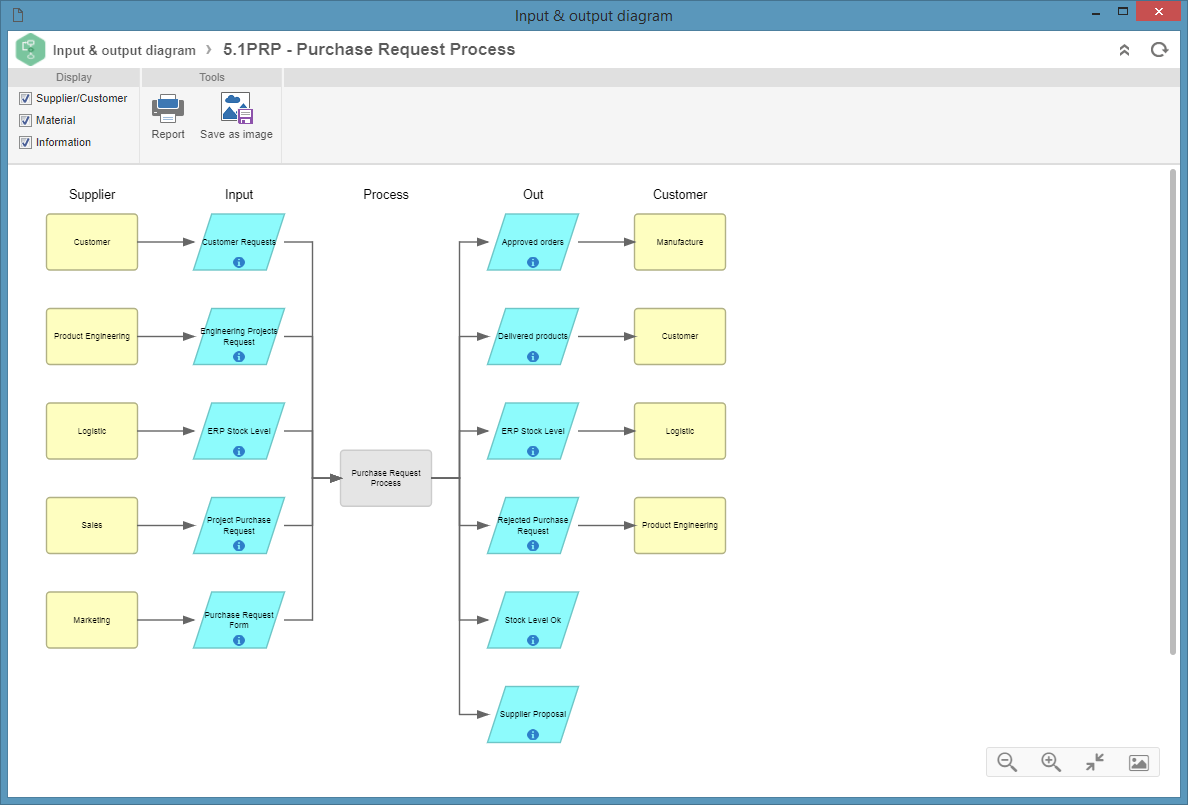
3. This diagram aims to present all the inputs and outputs of materials and information that occurred in the process items, as well as stakeholders.
- Supplier: the Supplier column lists the suppliers of the materials/information referring to each input. Each rectangle in this region represents a supplier.
- Input: the Input column displays all the information or materials used by the process. Each parallelogram in this region represents an input. Click on the item to open its data screen.
- Output: the Output column displays all the information or materials generated by the process. Each parallelogram in this region represents an output. Click on the item to open its data screen.
-
Process: the Process column displays the process item. If this process has sub-processes, they may be viewed (in an input & output diagram, or a new tab) when expanding the process through the
 icon. Click on the item to open its data screen.
icon. Click on the item to open its data screen. - Customer: the Customer column lists the customers that acquire the input materials and information. Each rectangle in this region represents a customer.
Note that the input and output information and material are associated on the process or activity data screens.
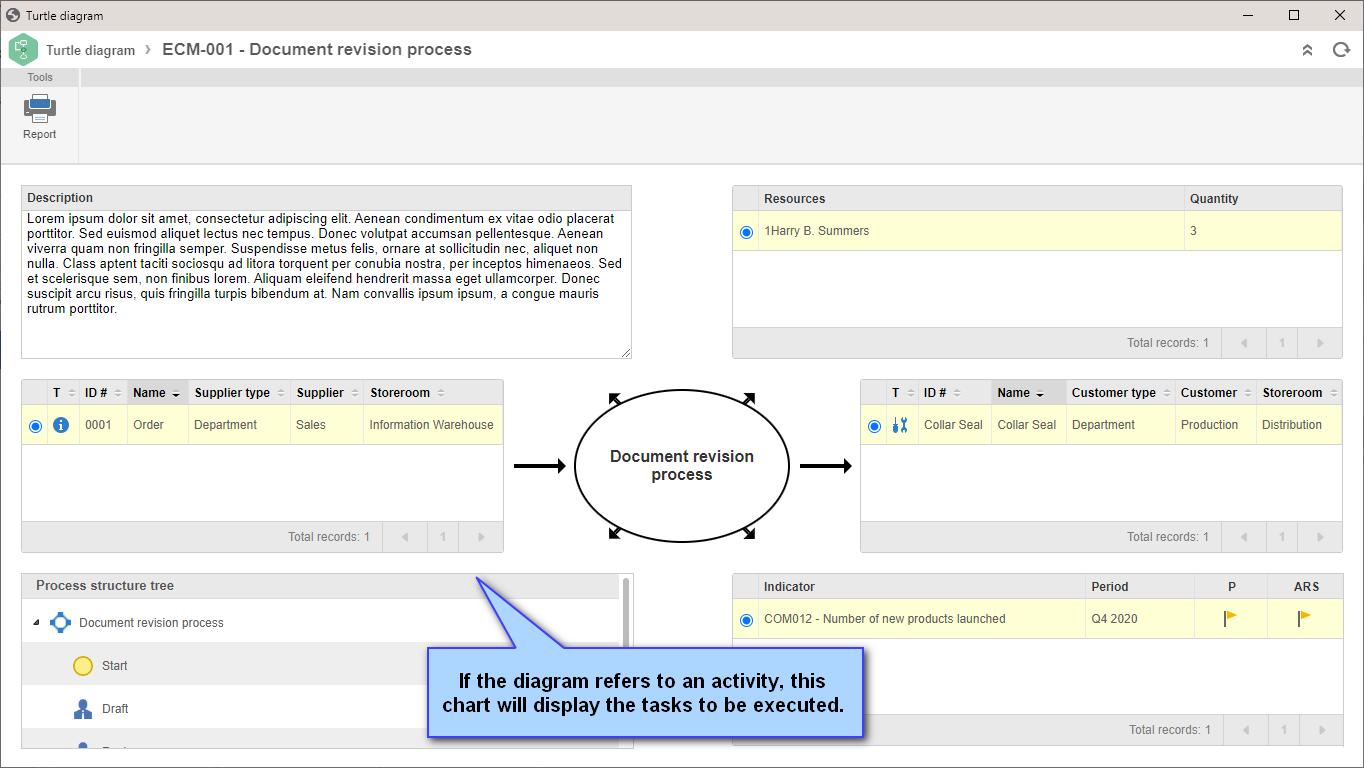
Turtle diagram
The Turtle diagram is an analysis tool that can be applied to all types of activities, decisions, and processes identified in the organization.
Each diagram has six boxes that focus on the process execution, inputs, and outputs.
To view the turtle diagram of a process or activity, click on the  button, located on several system screens (referenced in this documentation).
button, located on several system screens (referenced in this documentation).
See an example of the diagram:
Process flowchart
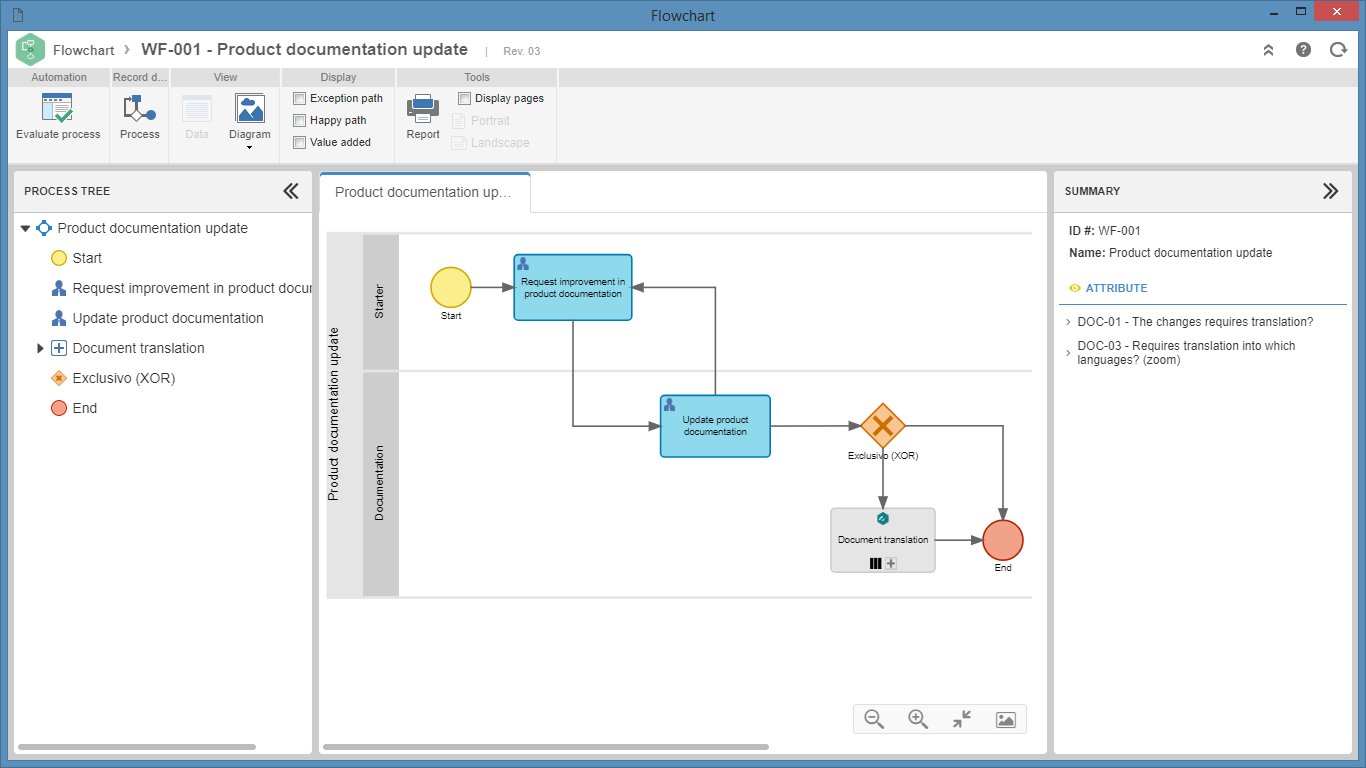
To view the flowchart of a process, click on the  button, located on several screens of the File, Management, and View menus and available in other components in which processes can be associated.
button, located on several screens of the File, Management, and View menus and available in other components in which processes can be associated.
When viewing the flowchart through the File > Process (PM022) menu, it will be possible to enable the process for editing, as long as the user has the proper permissions, and the process type has a simplified revision control. To do so, simply click on the Enable editing button, displayed on the flowchart screen and on the process data screen.
However, in processes whose types have ISO9000 or Workflow revision control, changes in the flowchart can only be performed by the drafter in the revision draft step.
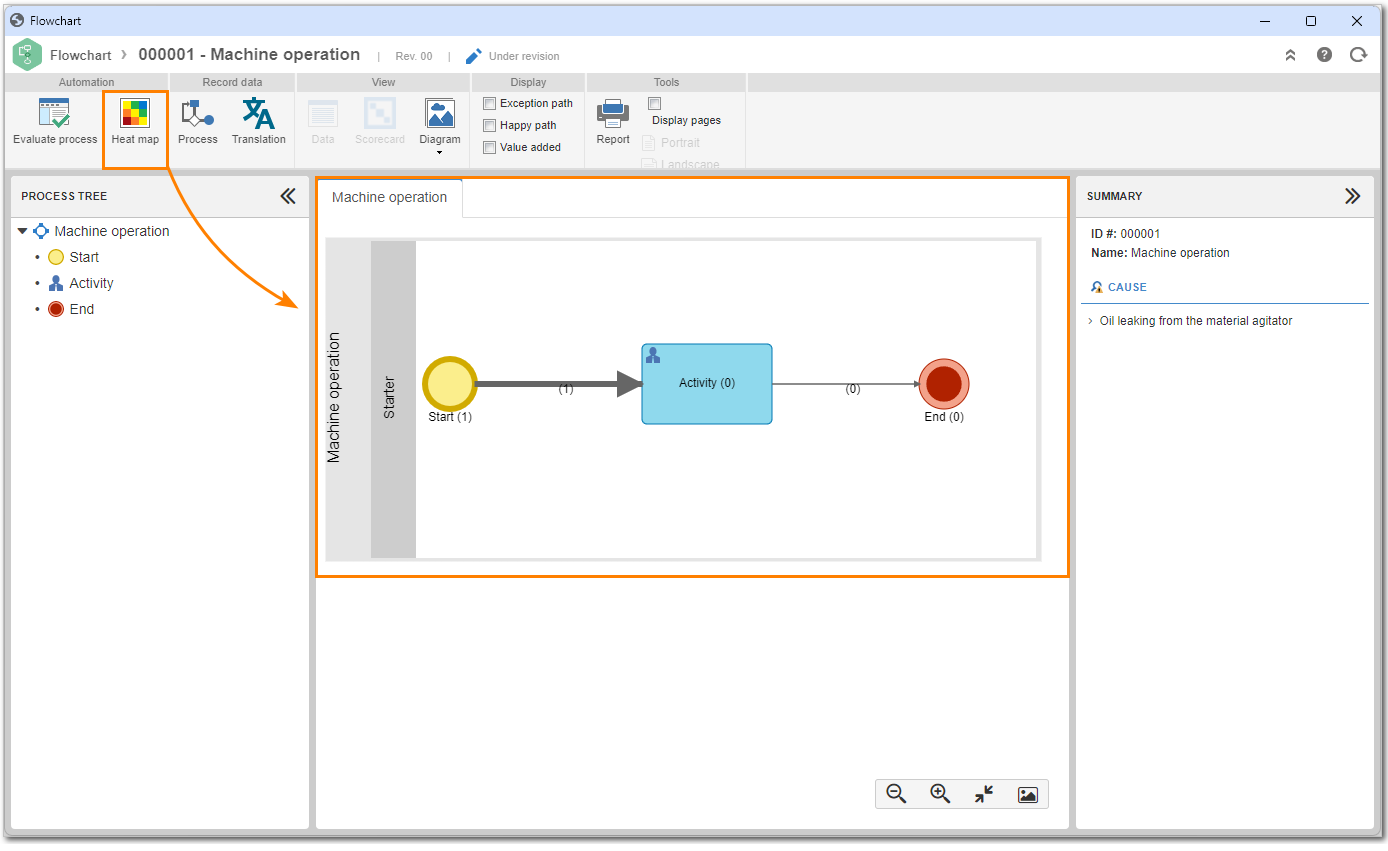
Below, see the flowchart of a process in the Process (PM023) menu:
Above the process flowchart, the Heat map button is displayed. This resource allows users to analyze the execution of process instances. This tool enables tracking the most accessed routes in the flowchart, checking which process steps work better and are more executed. Thus, it is possible to understand where improvements should be made and how failures can be avoided.
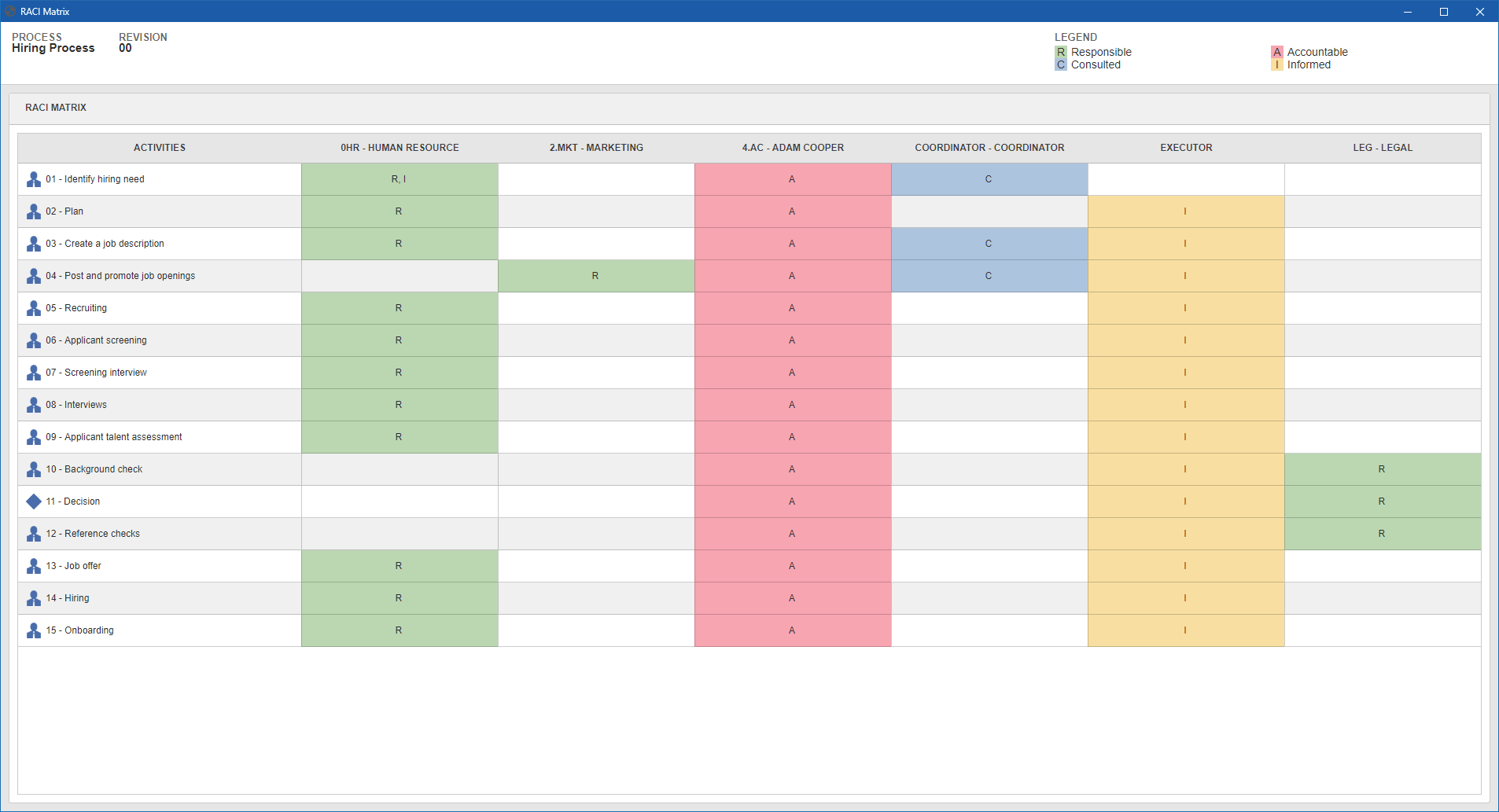
RACI Matrix
When discussing human resource management in the development of a project or process, the matter of the roles to be performed over time soon comes to mind. After all, it is unthinkable to track the schedule and manage the scope (and deliverables) without team members properly acknowledging their responsibilities in the project/process life cycle.
The best way to ensure processes will run smoothly is to map all parties involved, assigning functions to each person in the tasks to be performed. The RACI matrix is composed of an acronym, which also defines the roles and assignments of those involved.
| Responsible | Group of people (or individual) responsible for executing, developing, completing, and delivering the activity. |
| Accountable | Corresponds to the party with authority to organize the task, track its development and accept or formally reject a delivery. The accountable role is that of the approver, who will be held accountable for any deviations. Thus, there should only be one authority per task. |
| Consulted | Everyone who can provide tips, opinions, and suggestions to improve the development of the activity or enhance the deliverable. They must answer the questions of the responsible party, who, in their turn, must involve these people whenever necessary in order to add value or resolve doubts regarding the task being executed. |
| Informed | Everyone who must receive information on the completion and start of an activity (or even of a delivery) that will generate impacting changes in the process. |
The RACI matrix can be accessed through both the process data screen and the  button available on the button bar of the process file and view menus. See below how the RACI Matrix is displayed:
button available on the button bar of the process file and view menus. See below how the RACI Matrix is displayed:
CMDB
The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) gathers relevant information about the components of an information system. It is mainly used in the IT services of an organization in situations that require detailed tracking of the relationship between assets and business processes.
In SoftExpert Process, the CMDB relationship structure can be accessed through the CMDB button located on the process data screen:
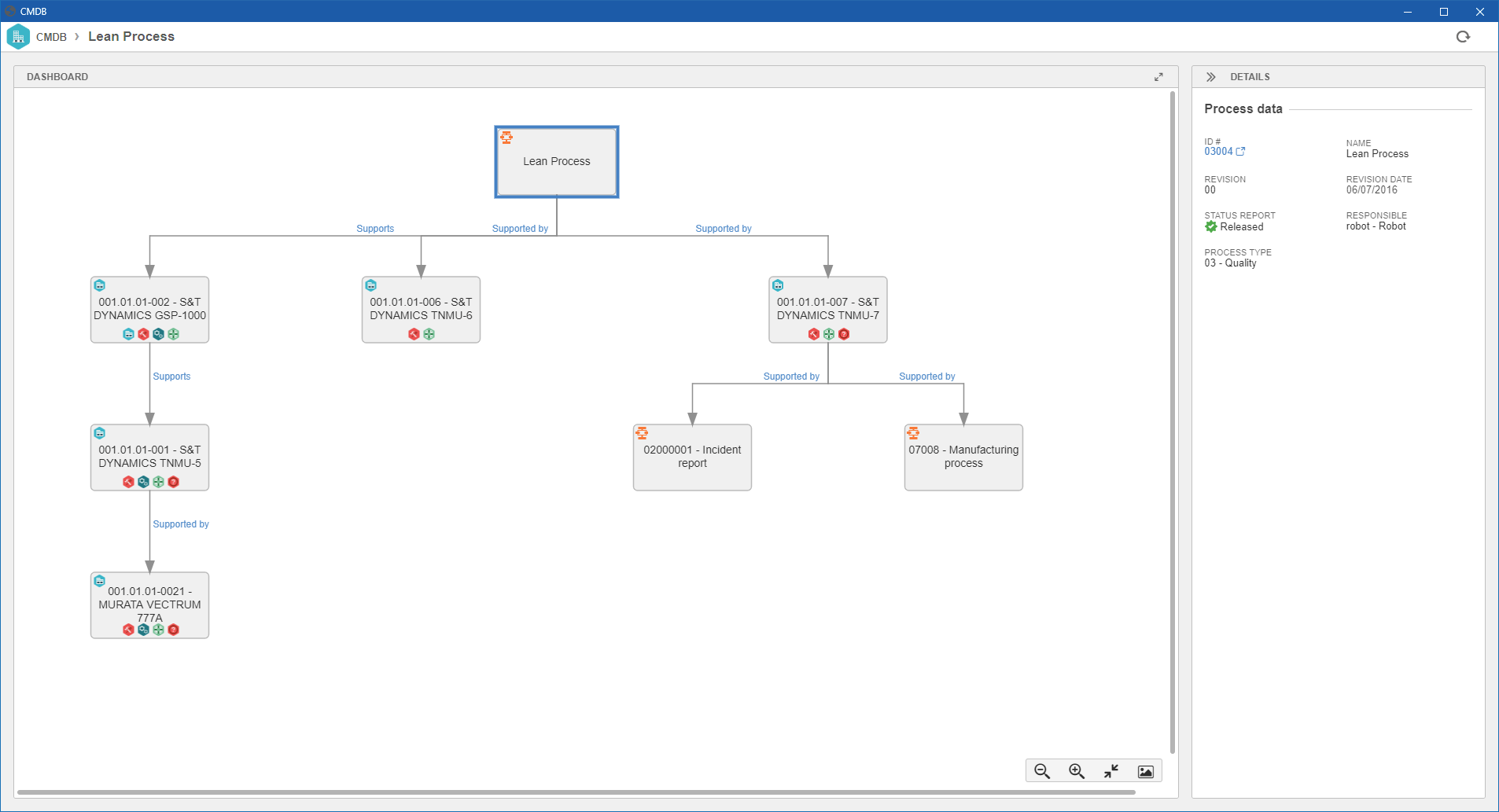
In SoftExpert Asset, the CMDB relationship structure can be accessed through the  button, located on the button bars of the following menus: Asset definition (AS016), View assets (AS030), and View computers (AS073).
button, located on the button bars of the following menus: Asset definition (AS016), View assets (AS030), and View computers (AS073).
The structure can also be viewed in the third quadrant of the menus mentioned above, through the Relationships option, which is available in the asset data screen.
Analyzing a process
To analyze a process, simply select it and click on the  button located on the toolbar of the view screens of several SoftExpert resources. This feature integrated with the Analytics component allows for creating analytical visions of the process for better control and planning of the procedure.
button located on the toolbar of the view screens of several SoftExpert resources. This feature integrated with the Analytics component allows for creating analytical visions of the process for better control and planning of the procedure.
Generating a report
To generate a report, click on the arrow next to the ![]() button. Three report options will be displayed:
button. Three report options will be displayed:
- Process report: displays process-related data, such as ID #, name, revision number and date.
- Turtle diagram: visually displays process elements.
- Process structure report: displays process data or a summary, in addition to details. It is also possible to generate a report for the process and its sub-processes in a grouped manner.

If you wish to generate a process report or a turtle diagram, simply click on the corresponding option, and the file will be shown, just as in the example below:

With the report on screen, the following features are made available:
A - This option will only be available for reports of the New and Customized types, provided that the logged user has the Edit control allowed in the access list of the generated report. It allows for changing the editable parameters of the report, if there is any.
B - This option will only be available if the logged user has the Scheduling control allowed in the access list of the generated report. It allows for scheduling the submission of reports via e-mail to certain users.
C - It allows for changing the report language. After selecting the desired language, wait for the tokens to be reloaded in the report. Notice that the language of the records will not change.
D - It allows for creating a document from the report. In order for this resource to work correctly, SoftExpert Document must be part of the solutions acquired by your organization. Refer to the documentation of the Document component for further details on the screen that will open.
E - It allows for rotating the report clockwise.
F - It allows for downloading the report to the logged user's machine. On the screen that will open, specify the directory in which the report will be saved and change the name of the file, if necessary. The report will be saved in .pdf format.
G - It allows for printing the report. To this end, a screen with the browser's printing options will open.
H - It allows for fitting the report to the viewer's screen size.
I - It allows for zooming in on the report.
J - It allows for zooming out on the report.

The process structure report allows for selecting which data will be displayed. Once the Process structure report option is clicked, a screen will open for this data to be selected.

After selecting the desired data, click on Generate report and the file will be shown.
Notice that not all features available in the other report types are enabled for the process structure report.

Sub-process report
To generate a sub-process report, access the Flowchart option and click on Report. On the screen that opens, use the Sub-processes field to add the information of the linked sub-processes to the report.

Conclusion
Thus, you have learned how to view several process data types!