Viewing a cause
Prerequisites
- Previously created and associated cause.
- Access to one of the following menus:
- Maintenance > View > Activity (MA011).
- Supply > View > Supply (SU012).
- Process > View > Process (PM023).
- Risk > View > Risk (RI502).
- PDM > View > Item (IT016).
- SPC > Execution > Data collection (SP006).
- FMEA > Management > FMEA (FM012).
- Workflow > Management > Workflow (WF004).
Introduction
Once the cause is created and associated, it can be viewed. By viewing a cause, it is possible to check how the cause of the nonconformity was related to the process, item, activity, or workflow.
See below how to view a cause in the components that make use of this resource:
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Suite
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Maintenance
1. Access the View > Activity (MA011) menu and select the desired activity.
2. Click on the  button to view the data.
button to view the data.
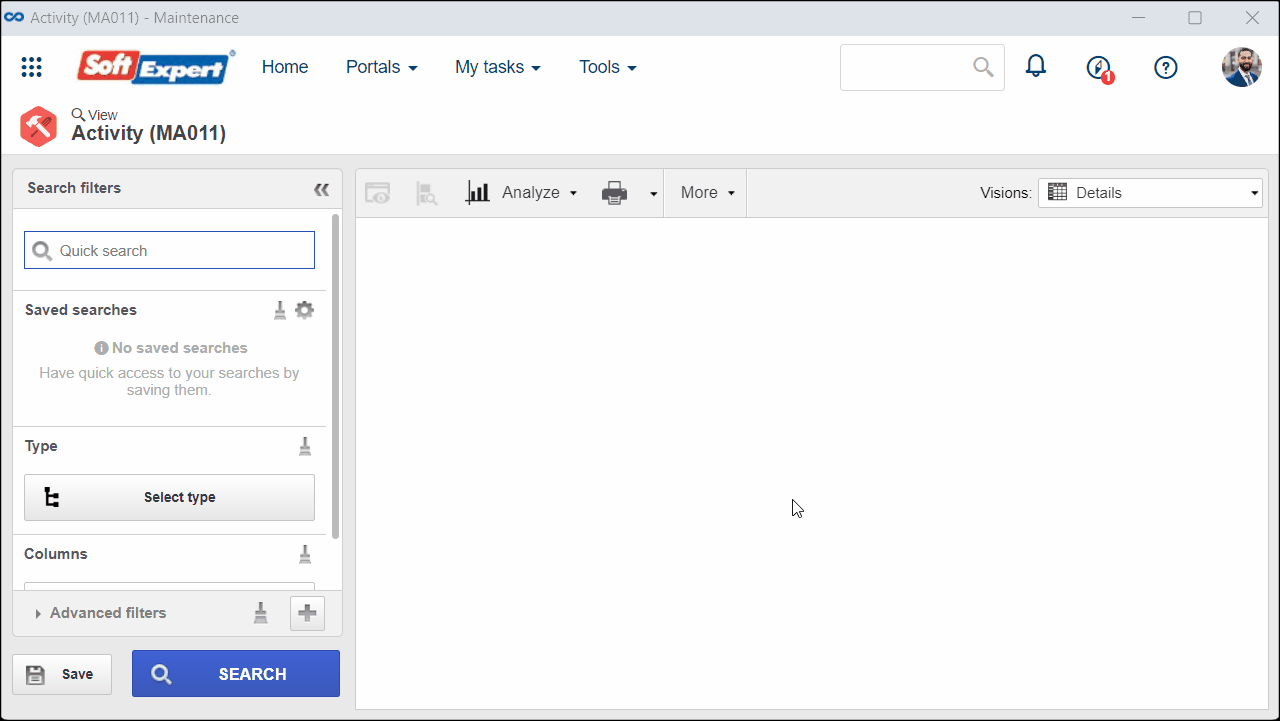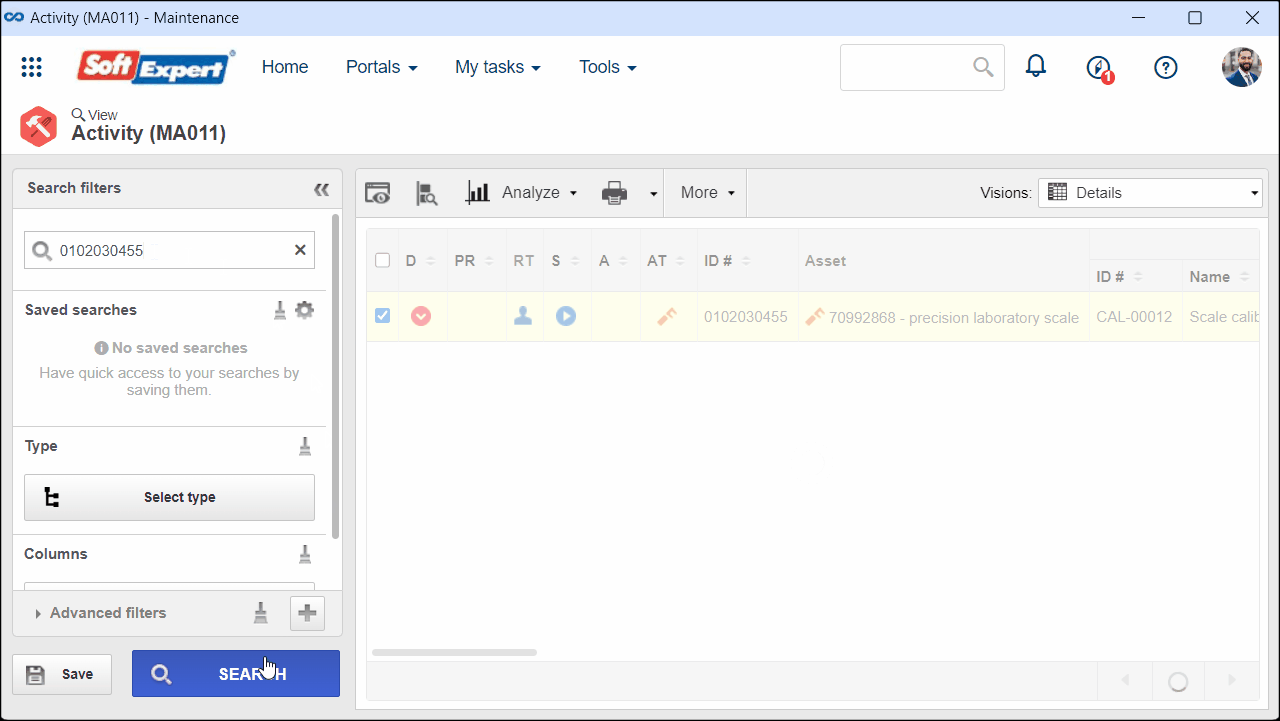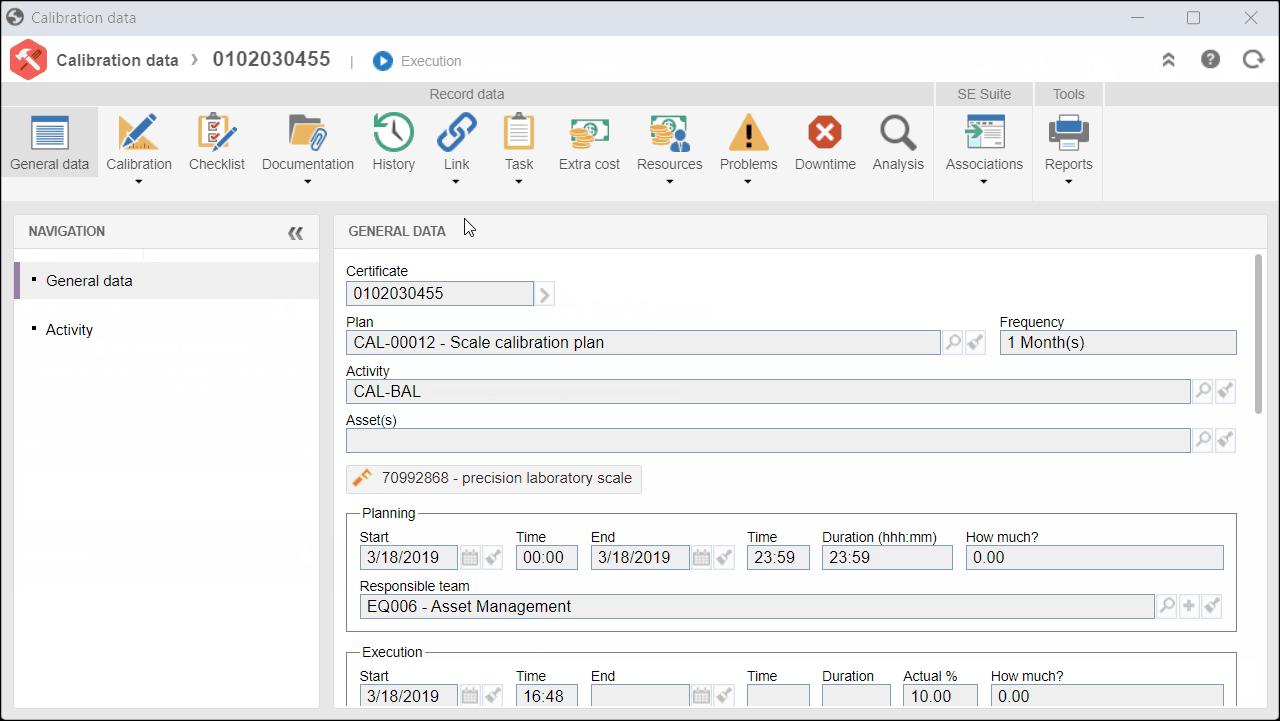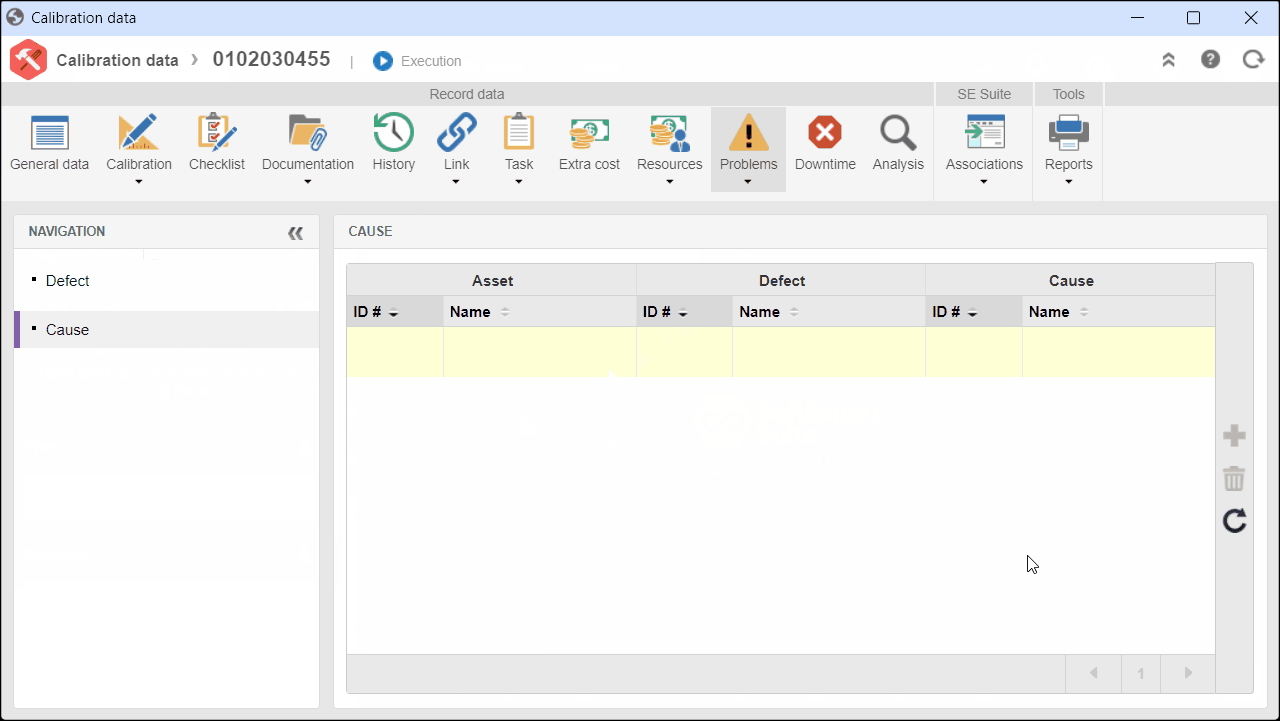
3. On the screen that will be opened, expand the Problems tab and click on Cause.
4. View the causes associated with the activity.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Supply
1. Access the View > Supply (SU012) menu and select the desired supply.
2. Click on the  button to view the data.
button to view the data.
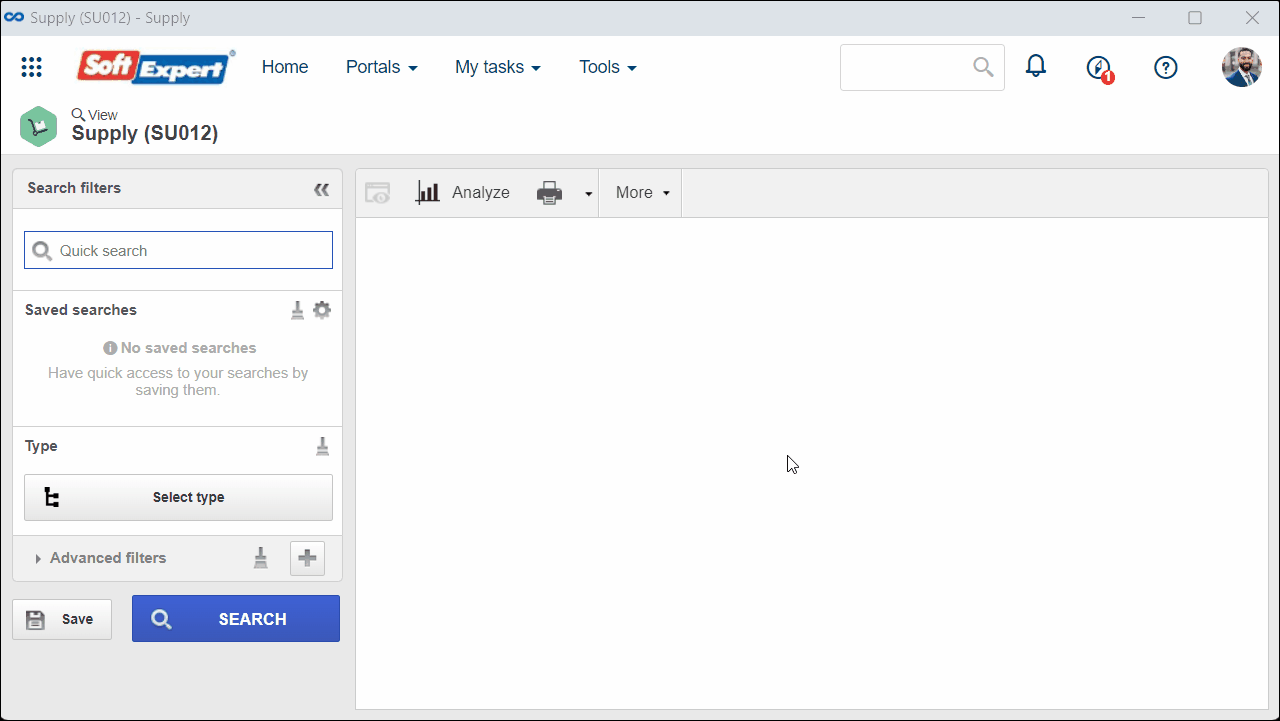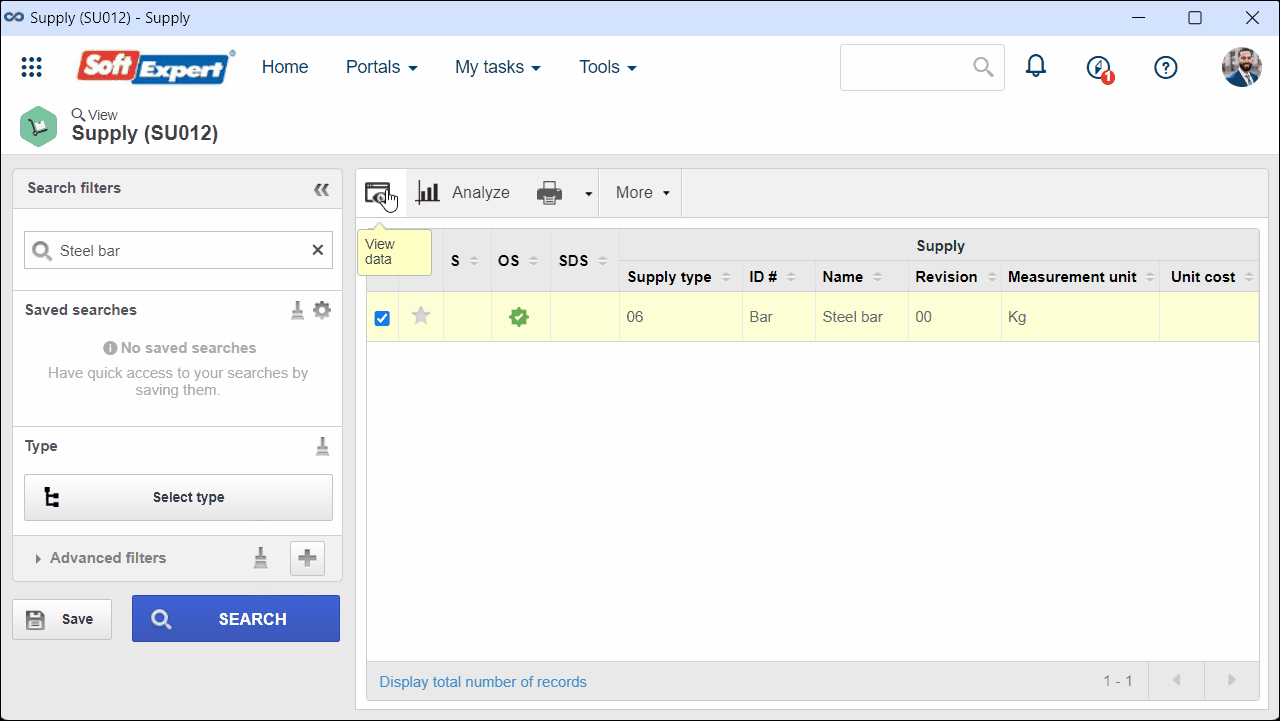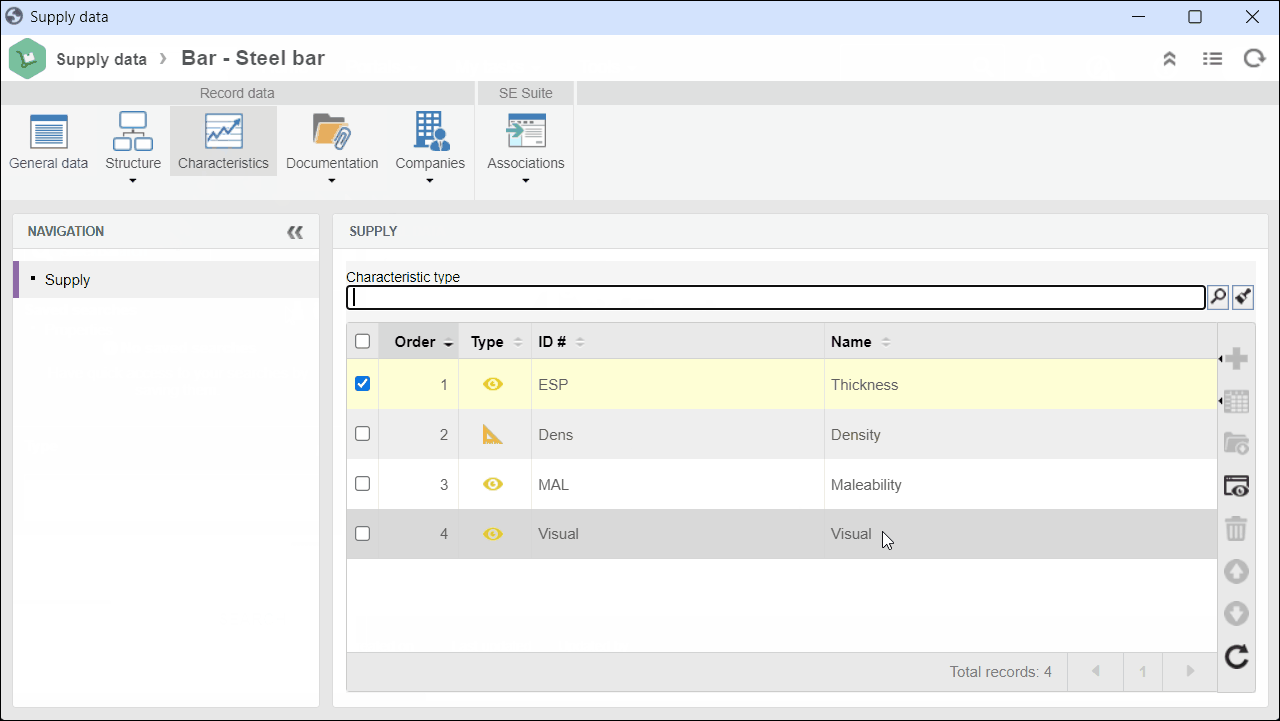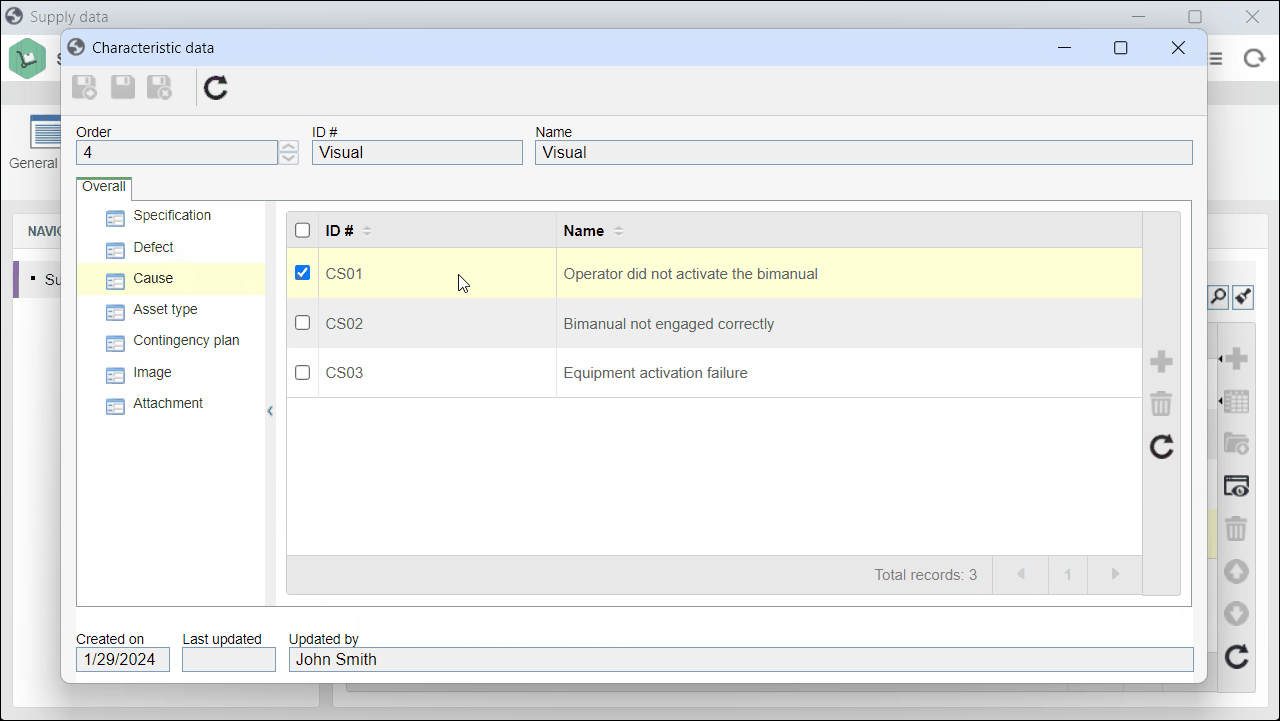
3. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Characteristic tab.
4. Select an attribute-type characteristic and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
5. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Cause section to view the associated causes.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Process
Viewing a cause in a process
1. Access the View > Process (PM023) menu and select the desired process.
2. Click on the  button to view the process data.
button to view the process data.
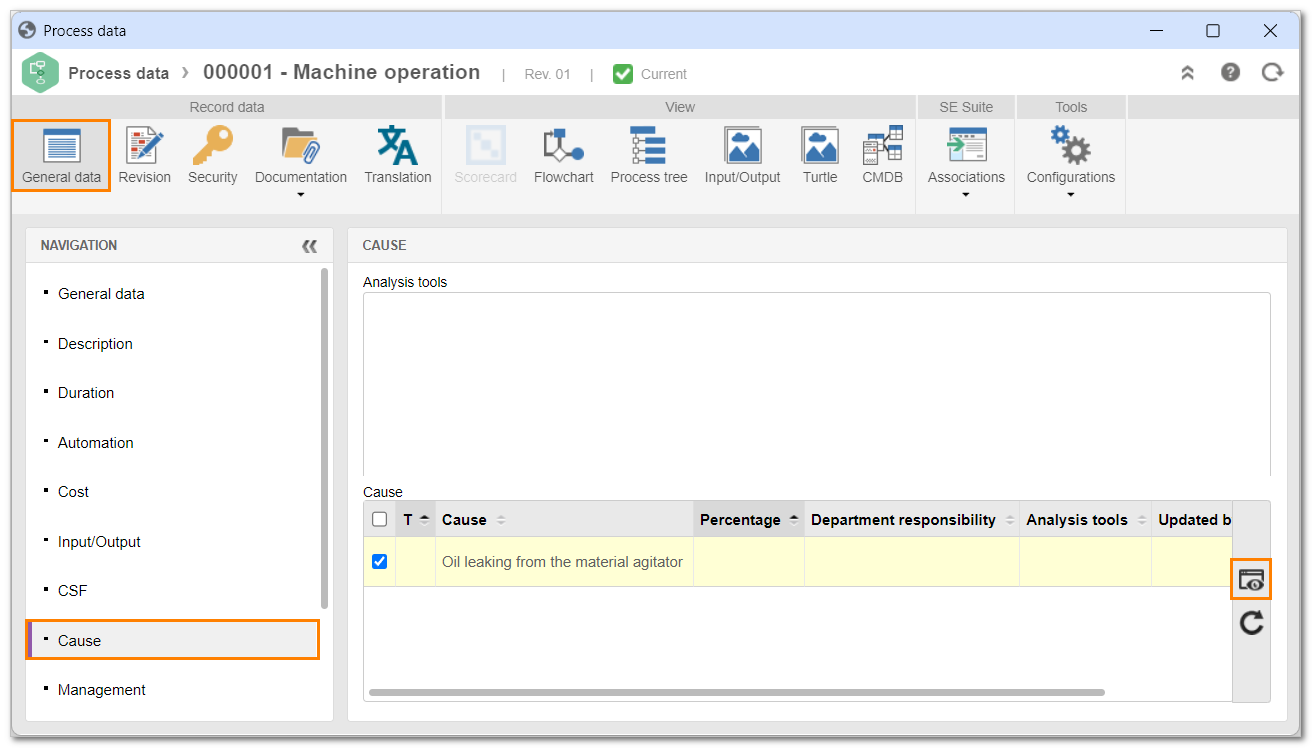
3. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Cause section of the General data tab.
4. Select the desired cause and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
Viewing a cause in a process activity
1. Access the View > Process (PM023) menu and select the desired process.
2. Click on the  button to open the process flowchart.
button to open the process flowchart.
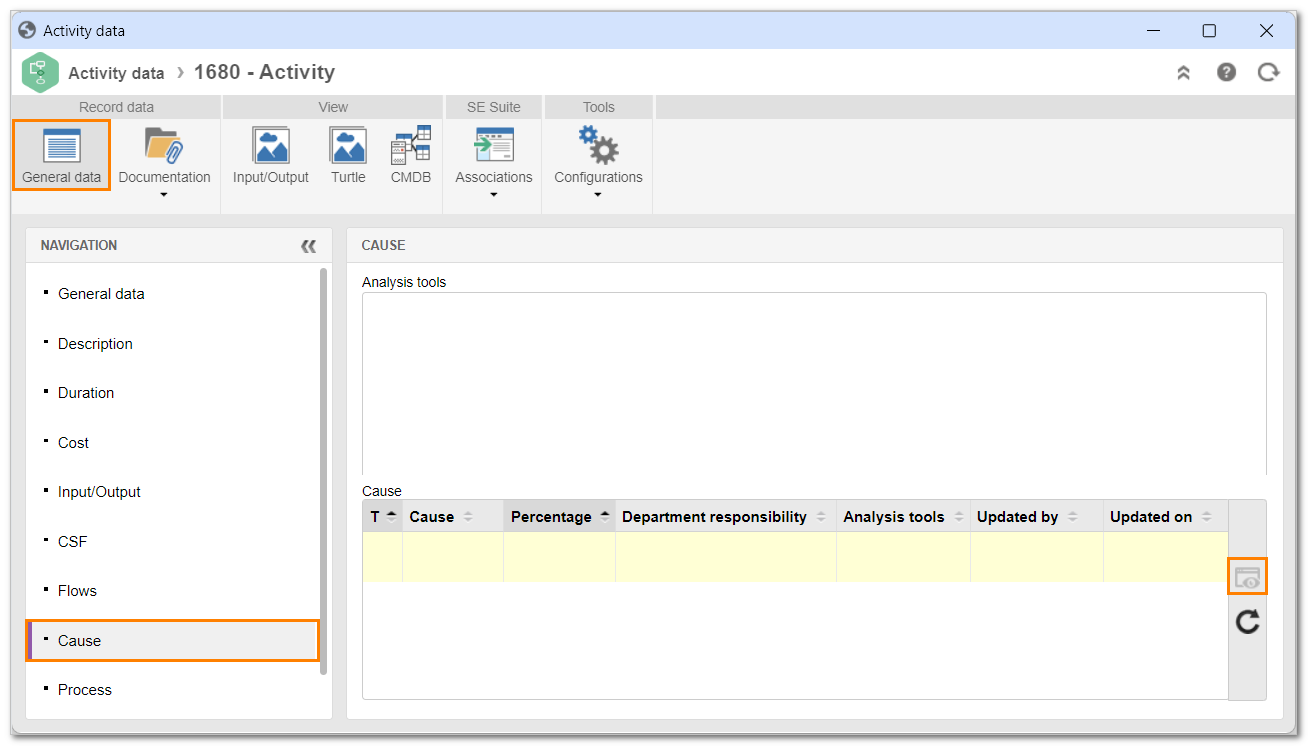
3. Select the desired activity in the flowchart and click on Data.
4. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Cause section of the General data tab.
5. Select the desired cause and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Risk
1. Access the View > Risk (RI502) menu and select the desired risk.
2. Click on the  button to view its data.
button to view its data.
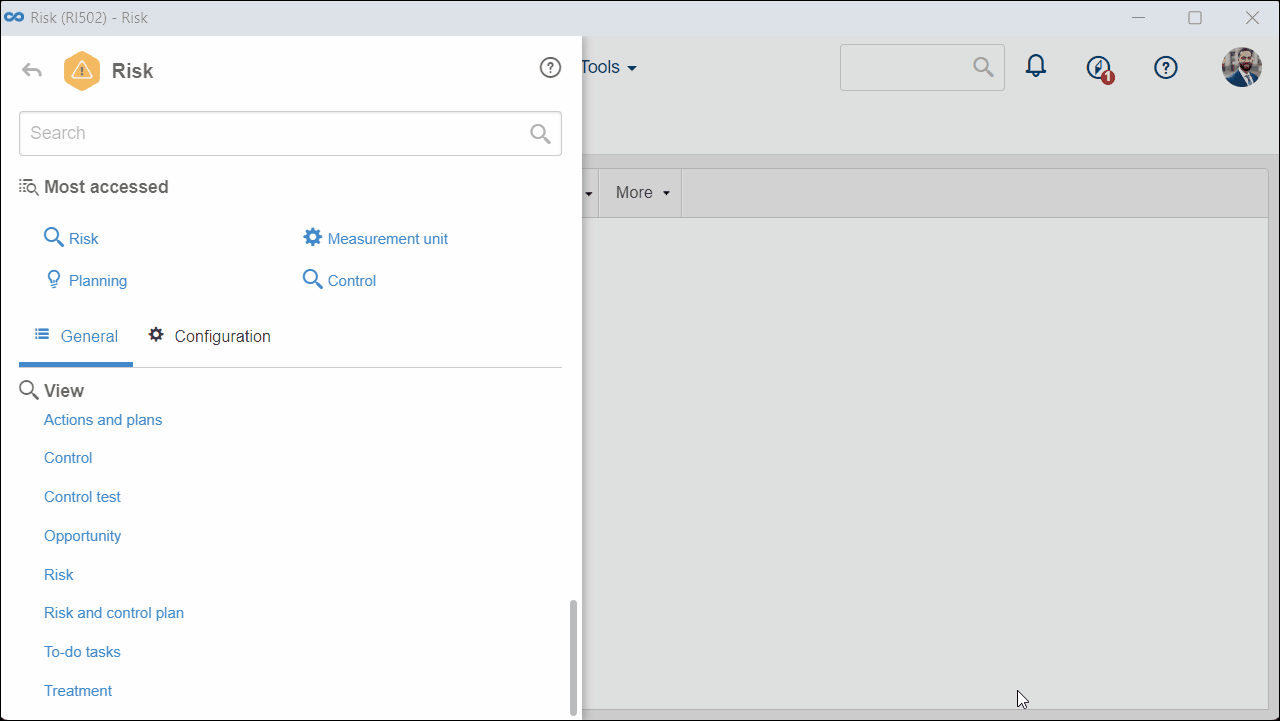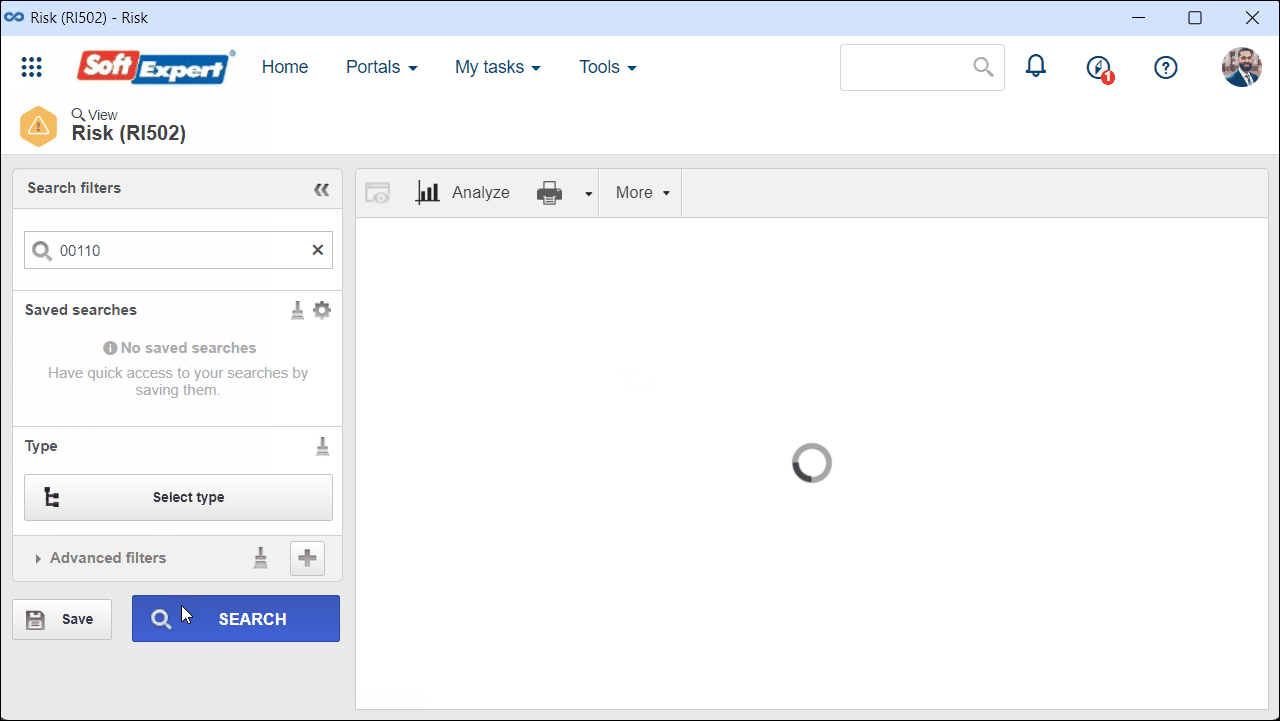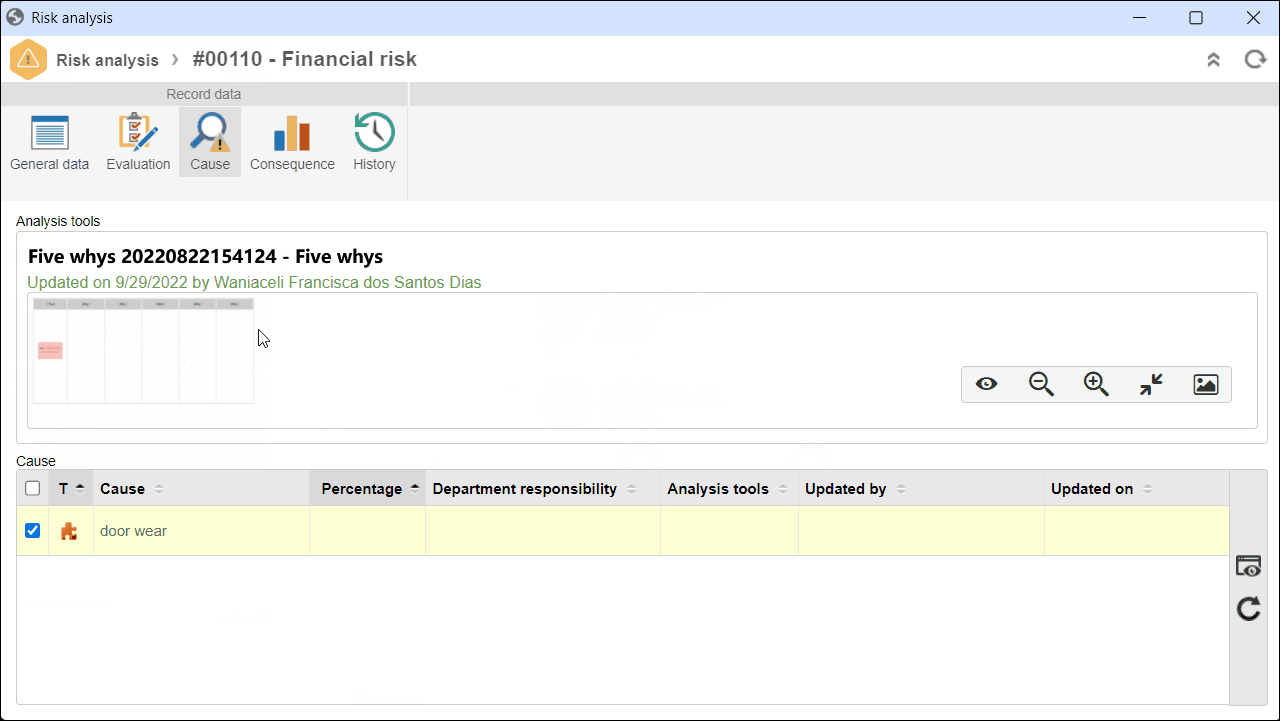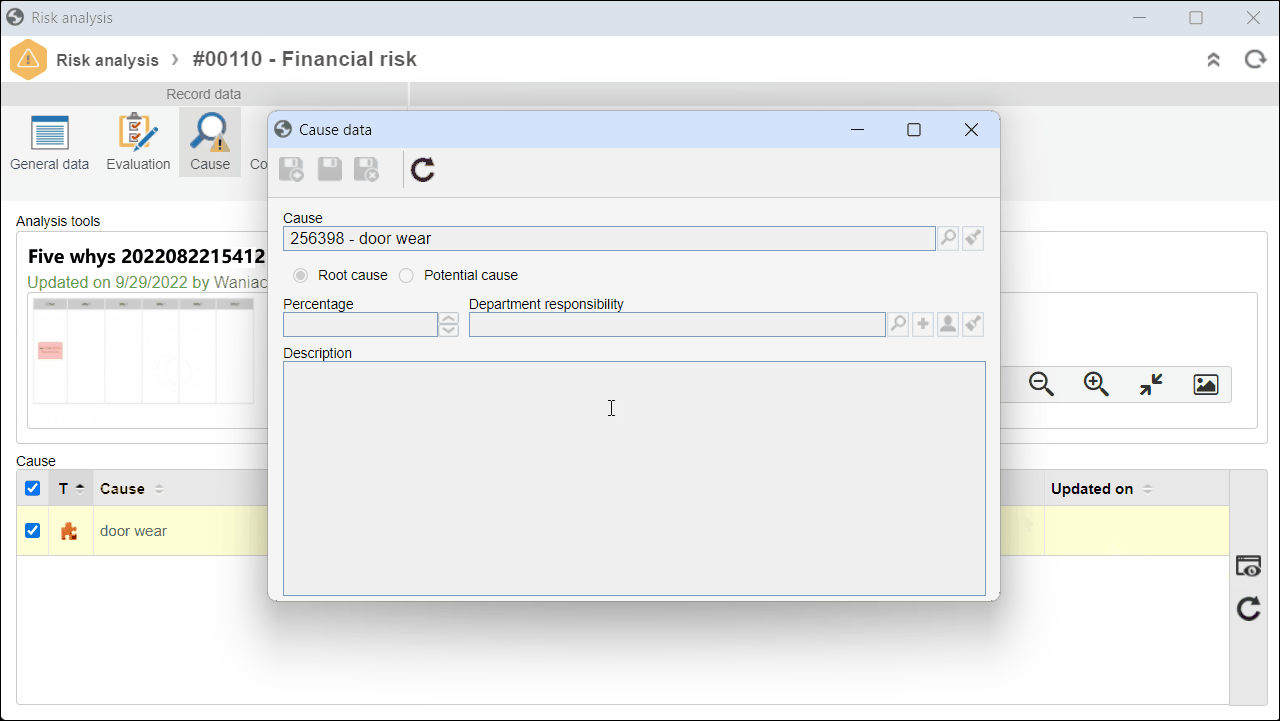
3. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Cause tab.
4. In the second quadrant, select a cause and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert PDM
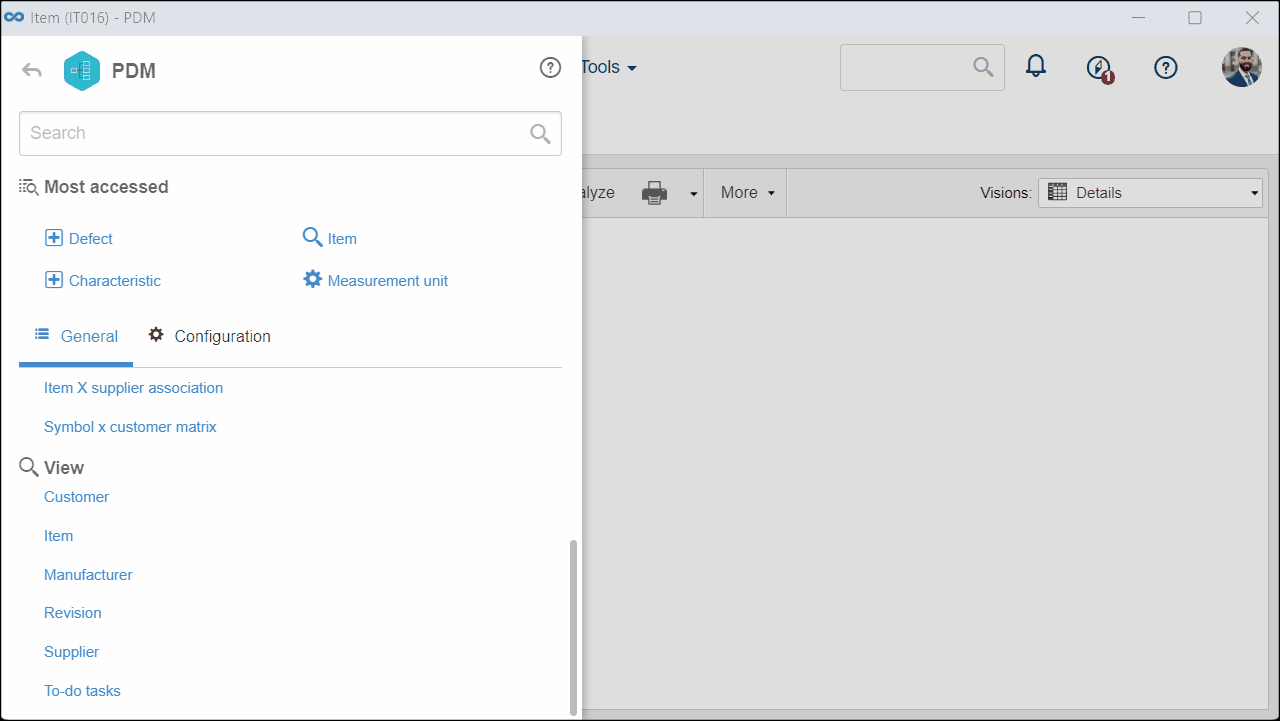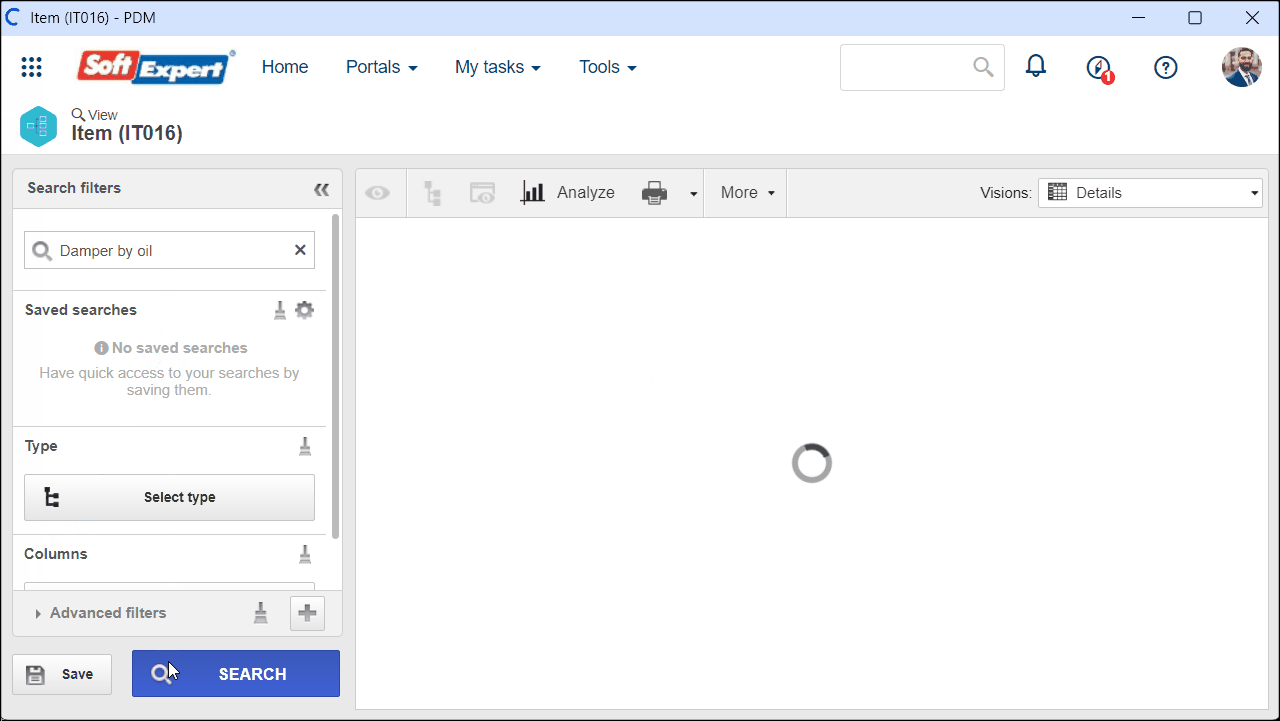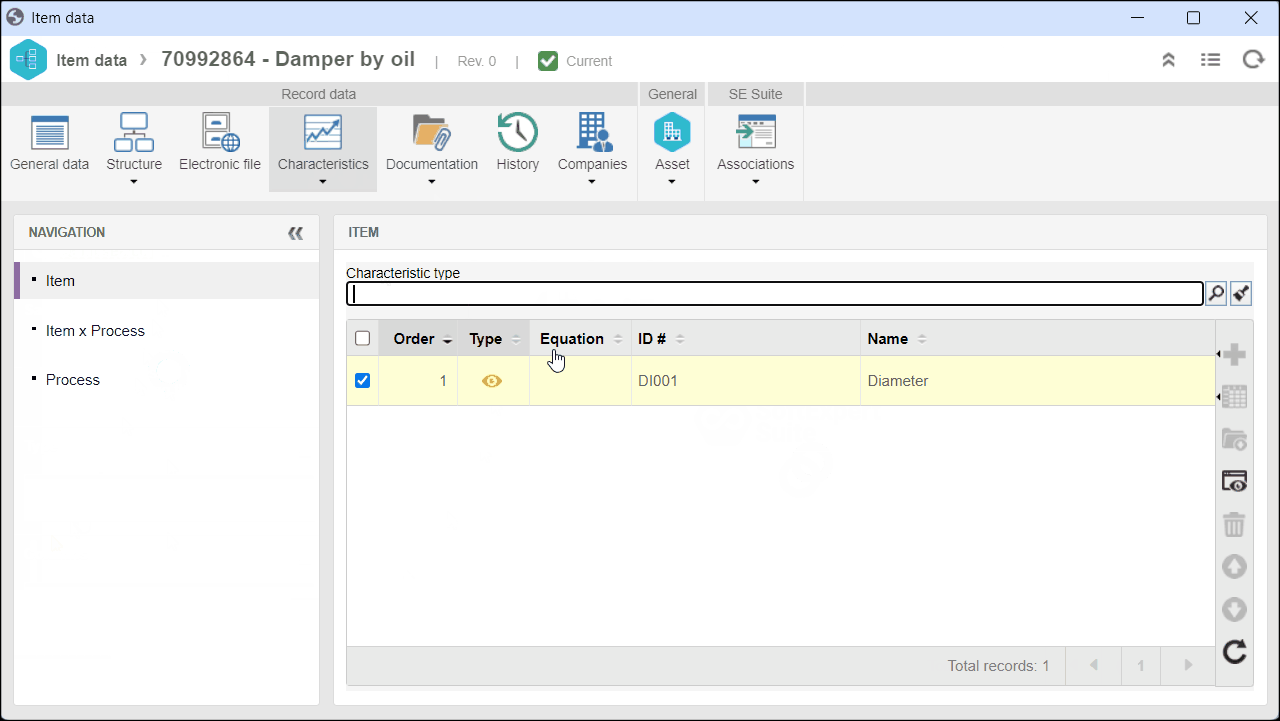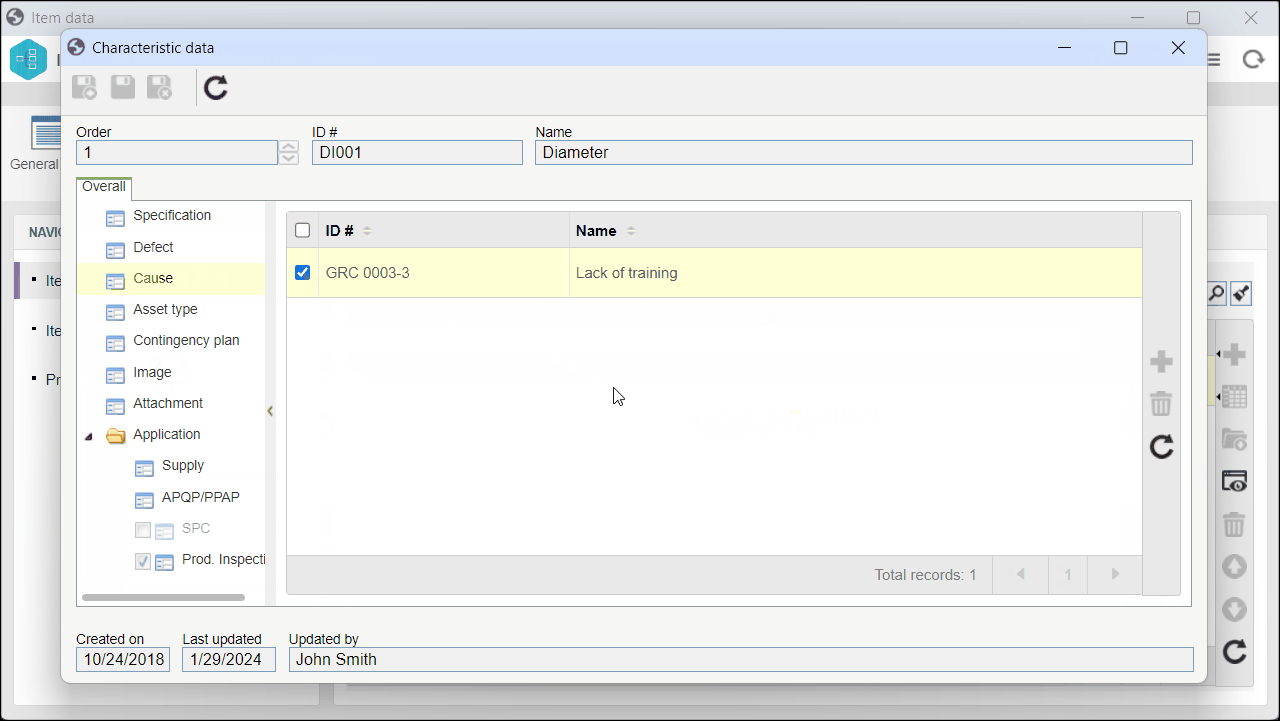
1. Access the View > Item (IT016) menu and select the desired item.
2. Click on the  button to view the item data.
button to view the item data.
3. On the screen that will be opened, expand the Characteristic tab and select Item.
4. Select the desired attribute-type characteristic in the Item field and click on  .
.
5. On the screen that will be opened, go to the Cause section to view the associated causes.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert SPC
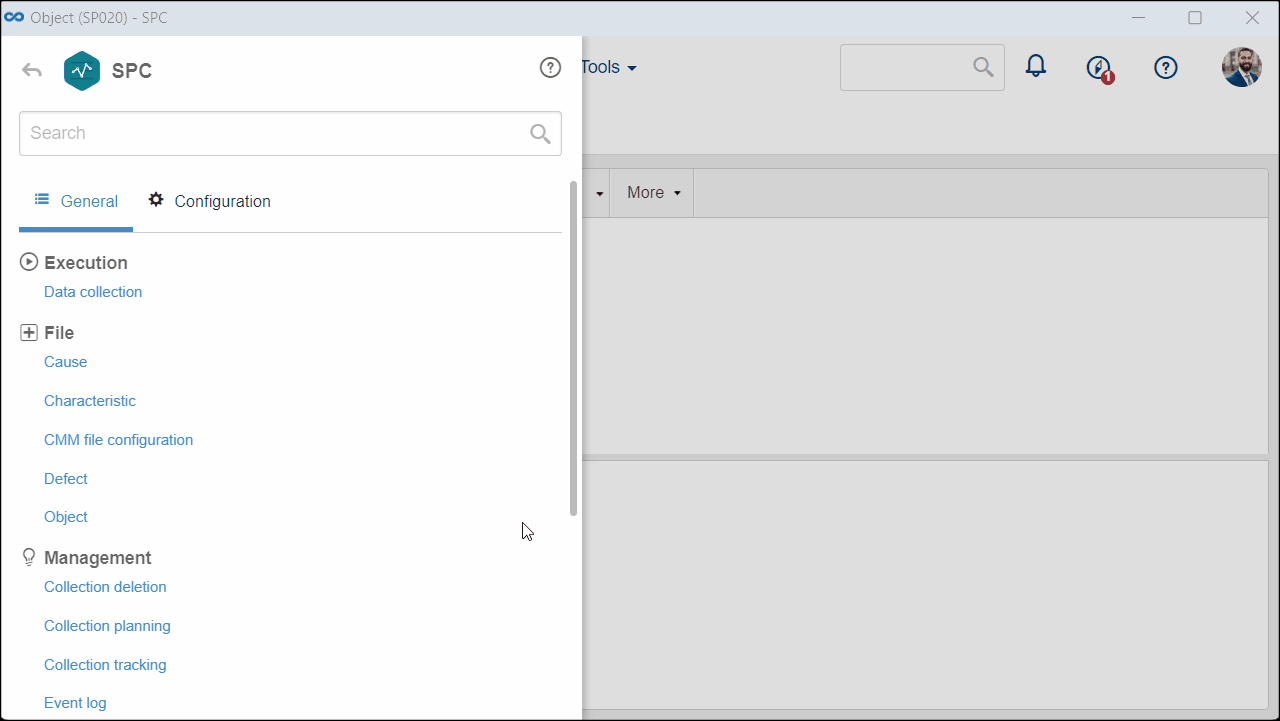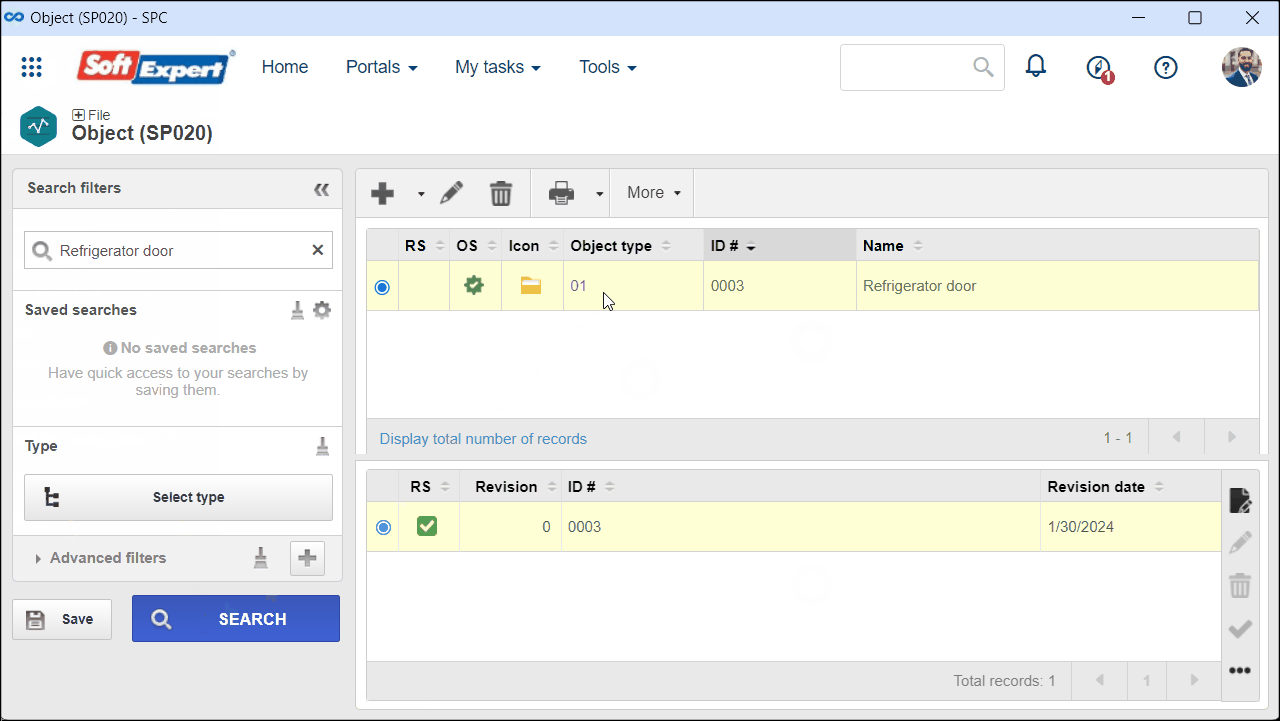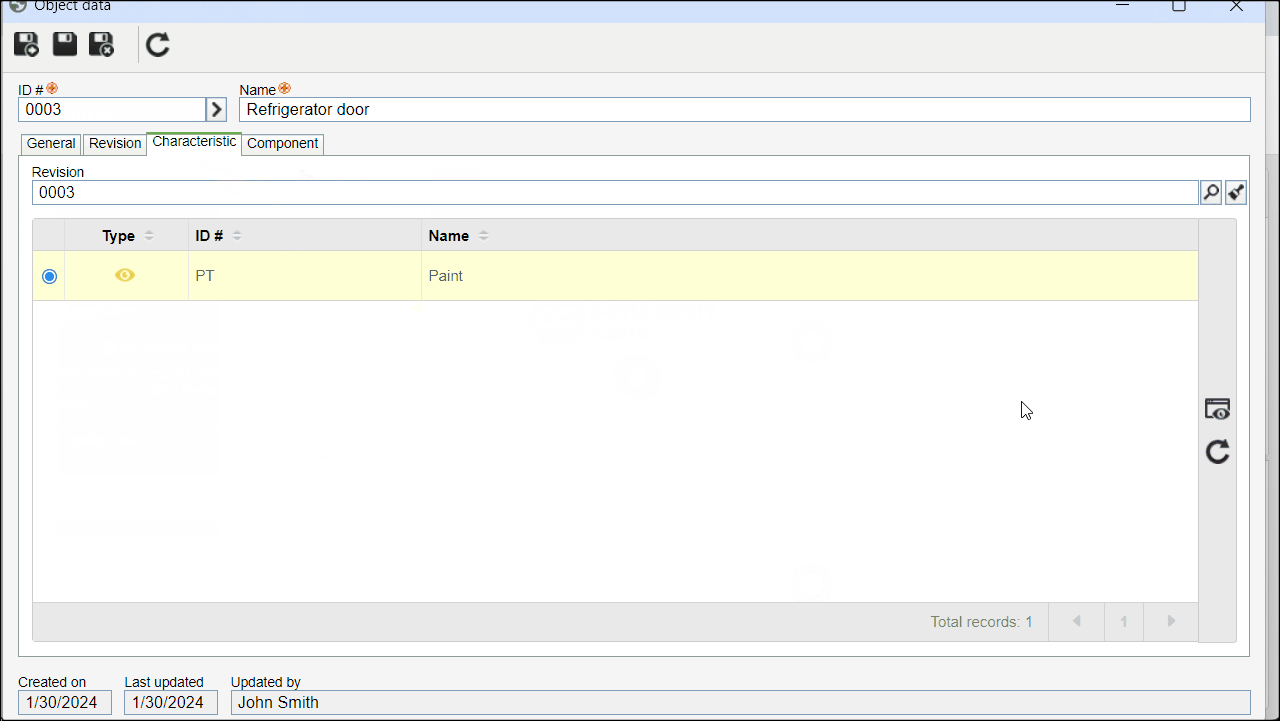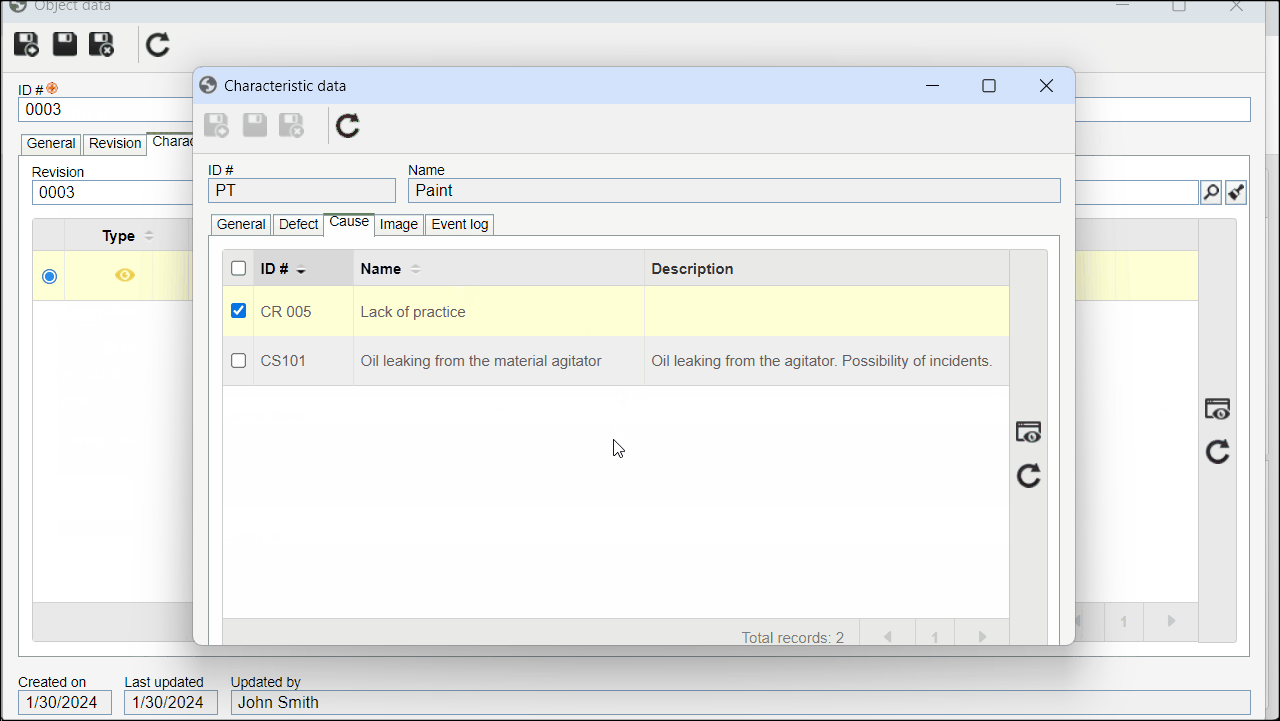
1. Access the File > Object (SP020) menu.
2. Select the desired object and click on the  button.
button.
3. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Characteristic tab.
4. Select an attribute-type characteristic and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
5. On the screen that will be opened, click on the Cause tab to view the associated causes.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert FMEA
1. Access the Management > FMEA (FM012) menu.
2. Select an FMEA of the AIAG PFMEA type and click on the  button.
button.
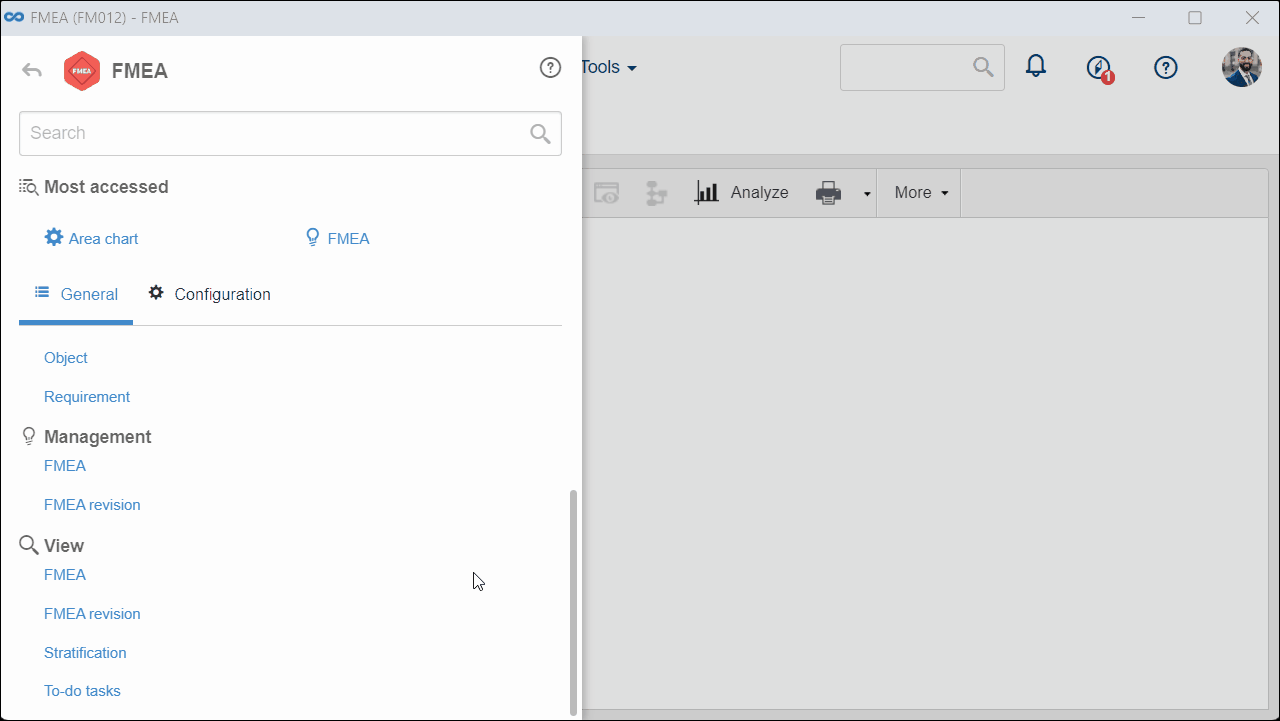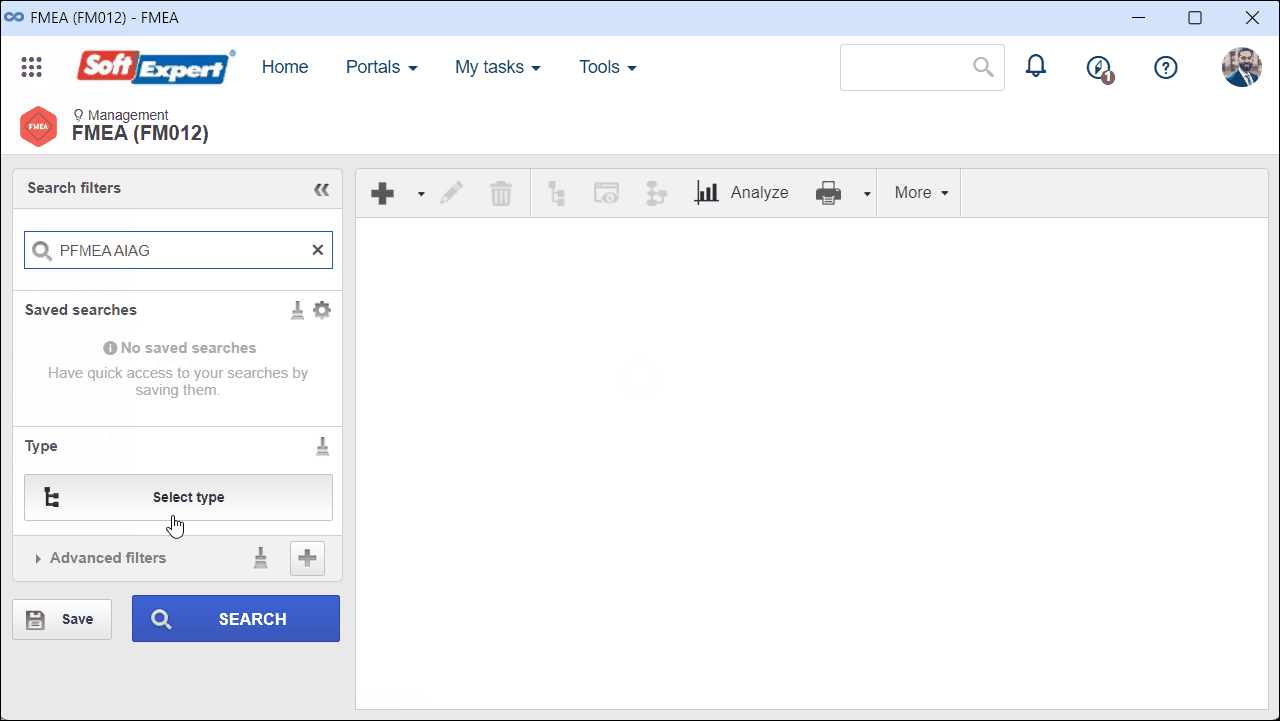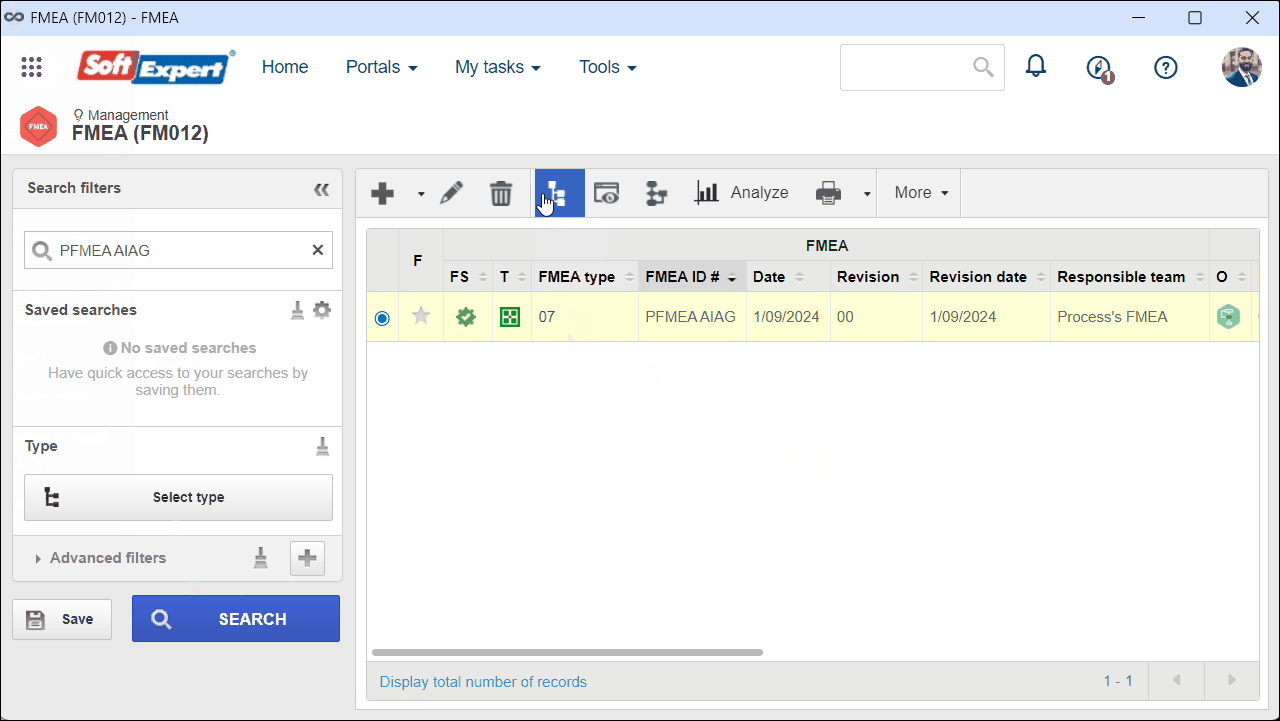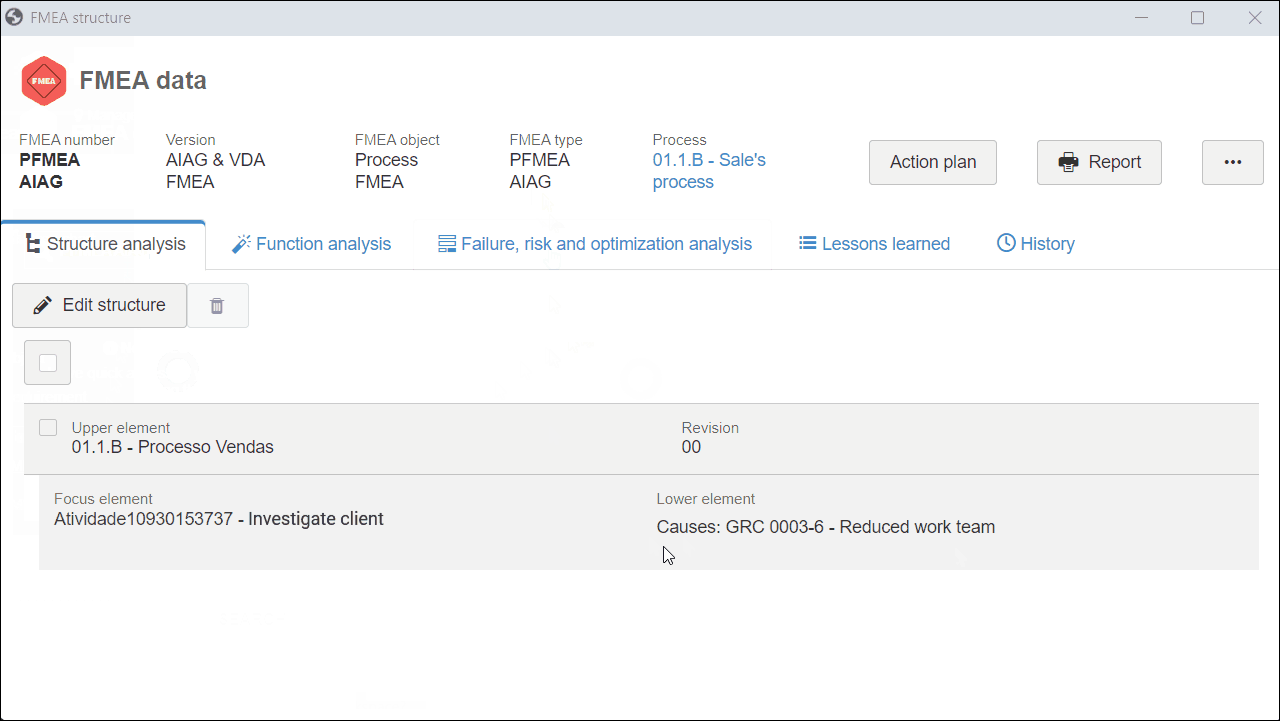
3. On the screen that will be opened, click on Upper element in the Structure analysis tab.
4. View the cause associated with the Upper element field that will be displayed.
Viewing a cause in SoftExpert Workflow
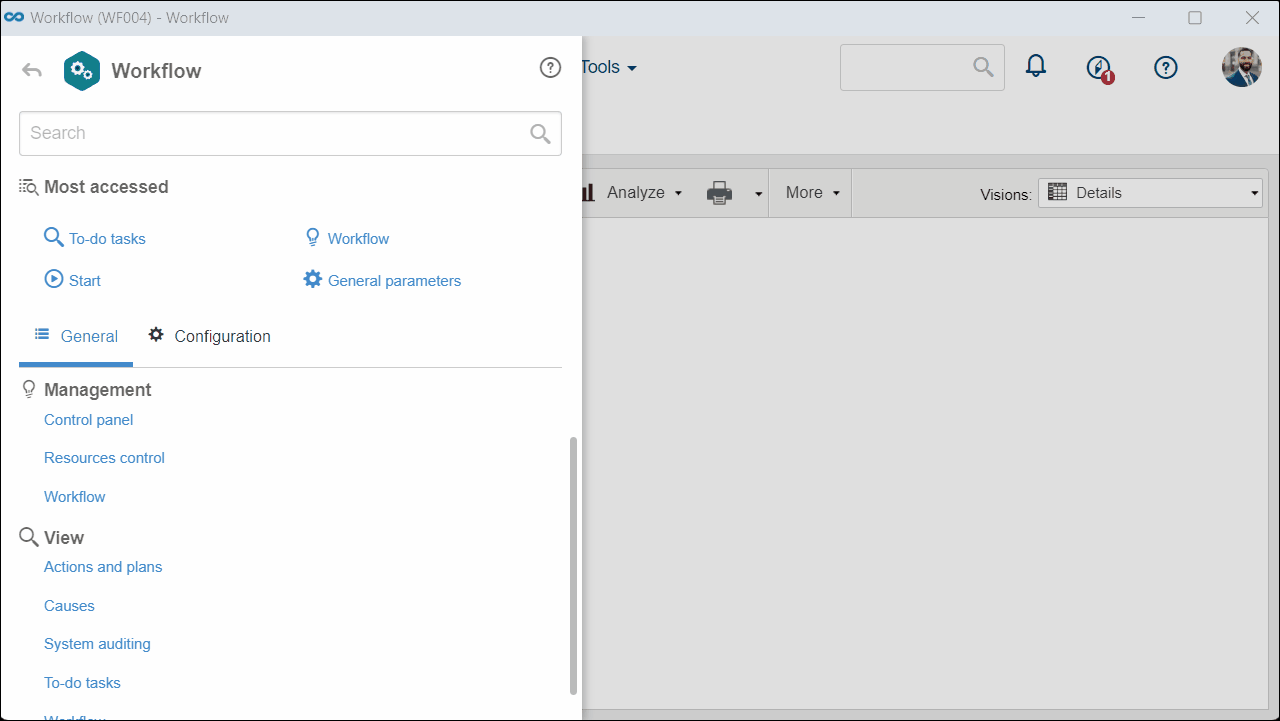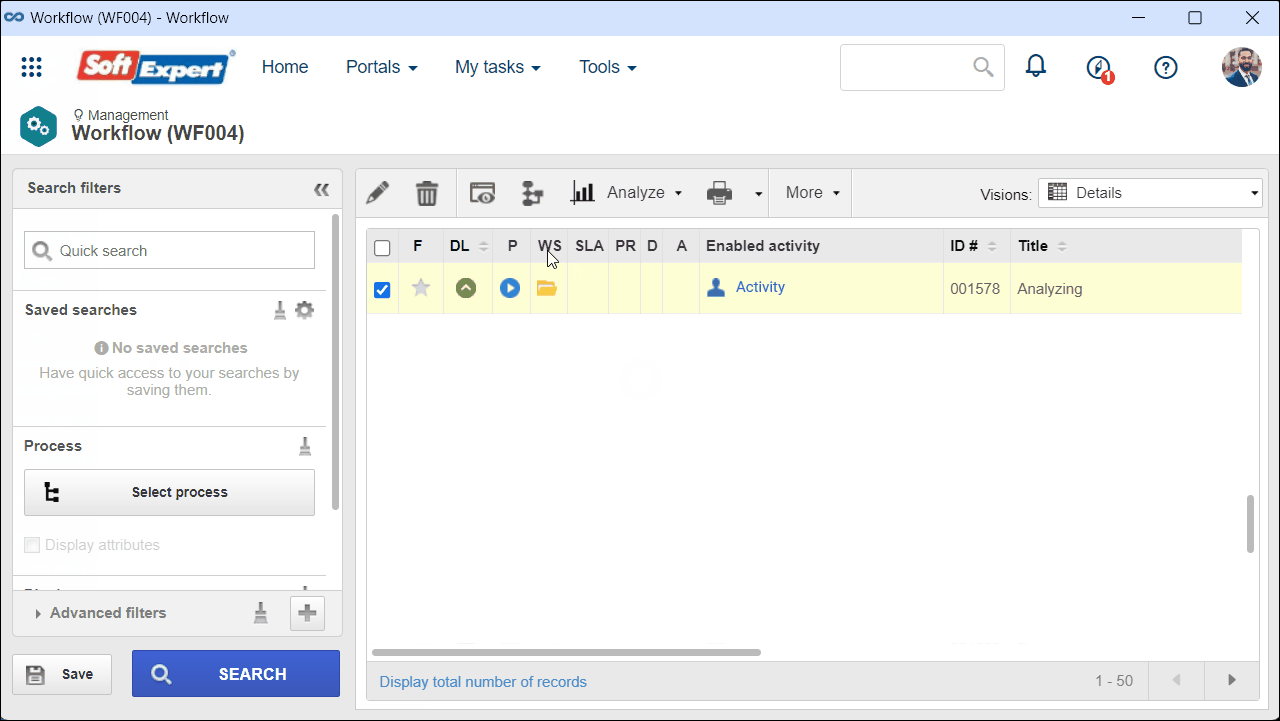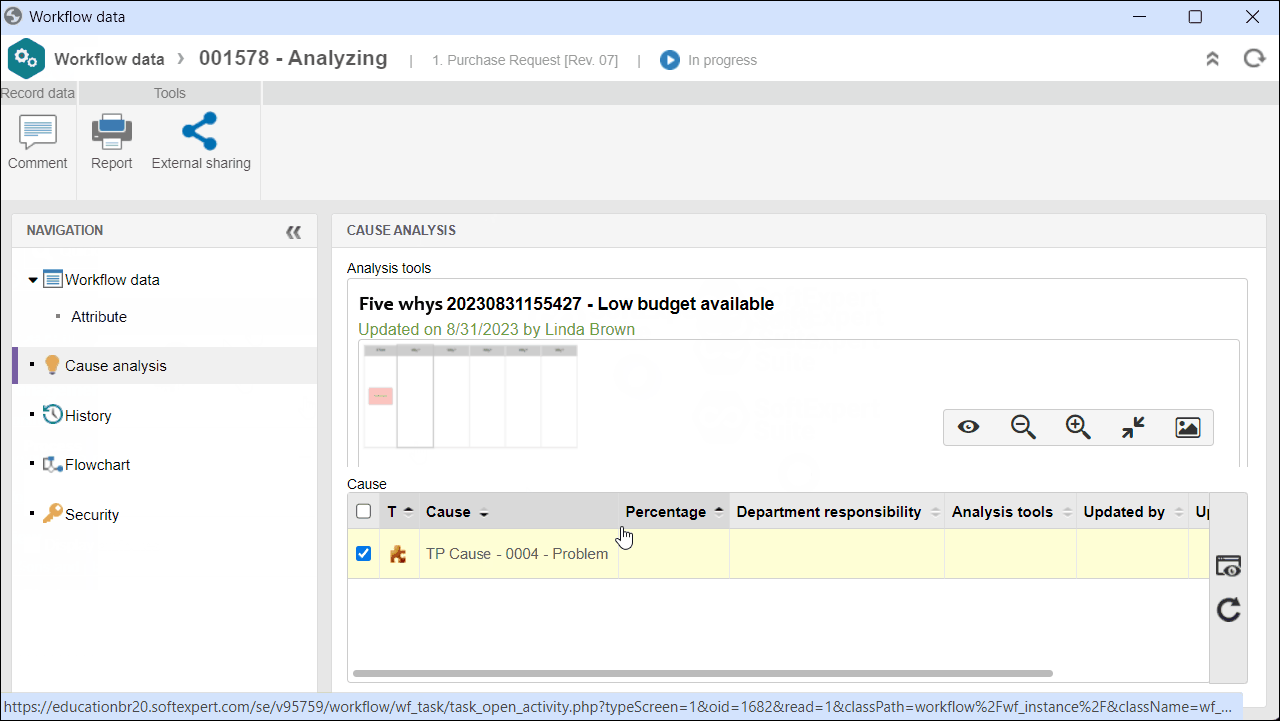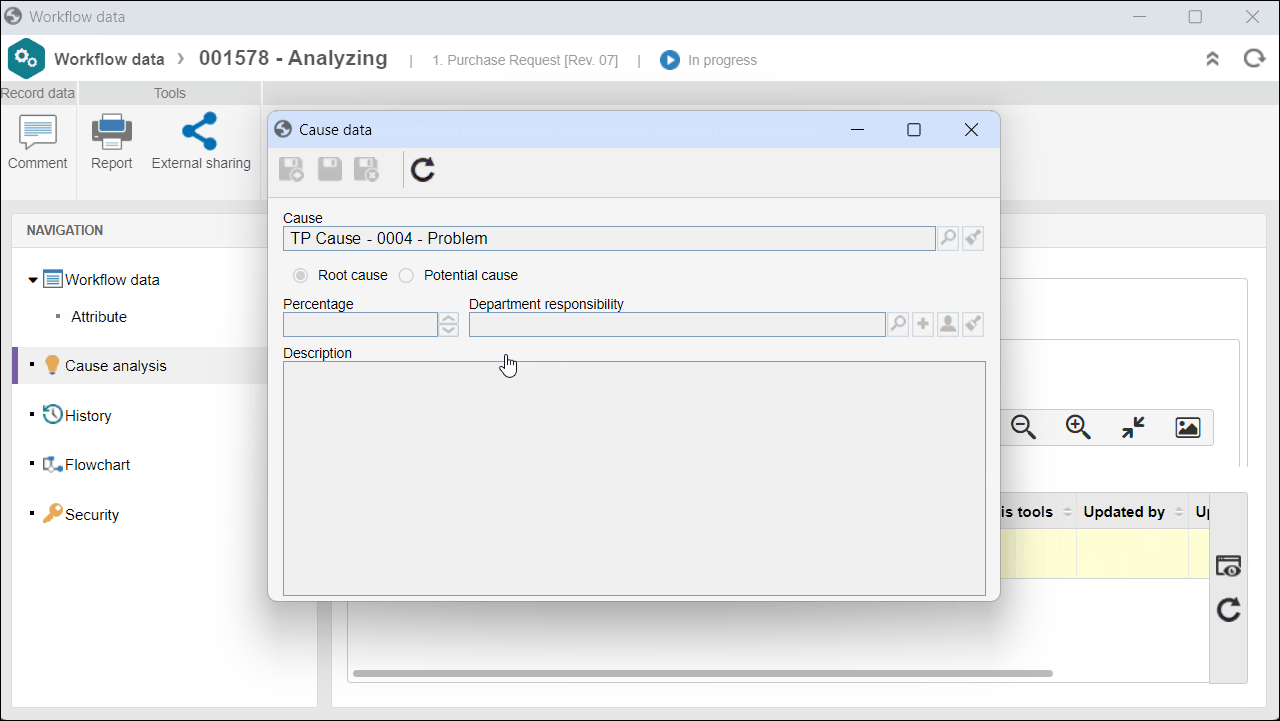
1. Access the Management > Workflow (WF004) menu.
2. Select the Workflow of the process in which the cause analysis was used and click on  .
.
3. On the screen that will be opened, access the Cause analysis tab.
4. In the second quadrant, select the desired cause and click on  to view its data.
to view its data.
Conclusion
Thus, we have viewed the associated cause and finished the flow of this resource. We can now explore the utility of this feature for the organizational process.